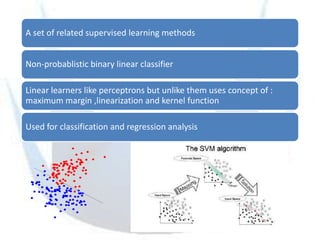
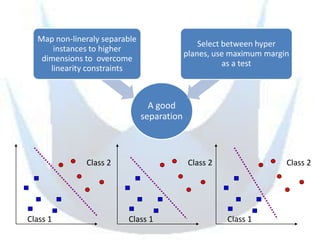
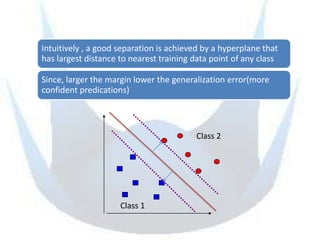
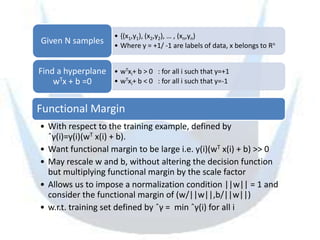
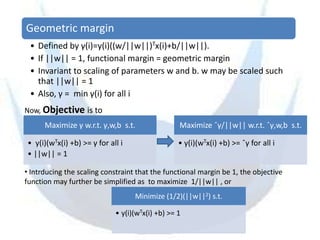
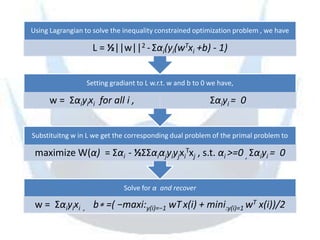
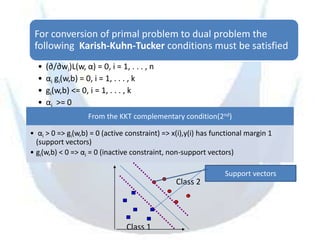
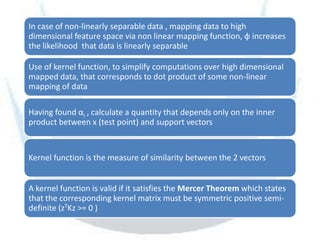
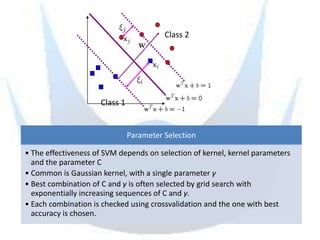
SVM is a supervised learning method that finds a hyperplane with maximum margin to separate classes. It uses kernels to map data to higher dimensions to allow for nonlinear separation. The objective is to minimize training error and model complexity by maximizing the margin between classes. SVMs solve a convex optimization problem that finds support vectors and determines the separating hyperplane using kernels, slack variables, and a cost parameter C to balance margin and errors. Parameter selection, like the kernel and its parameters, affects performance and is typically done through grid search and cross-validation.