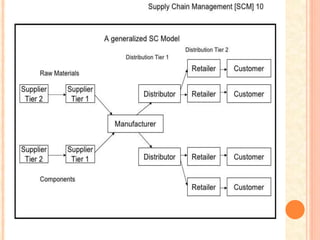
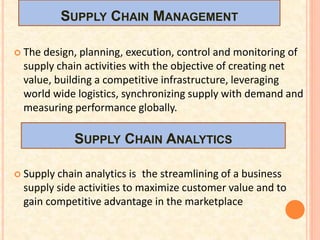
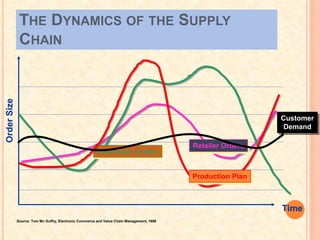
The document discusses supply chain management and analytics. It defines supply chain management as designing, planning, executing, controlling, and monitoring supply chain activities to create value and gain competitive advantage. Supply chain analytics refers to streamlining business supply-side activities to maximize customer value.
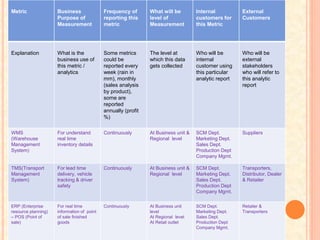
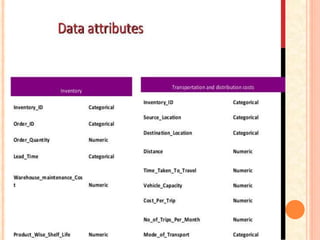
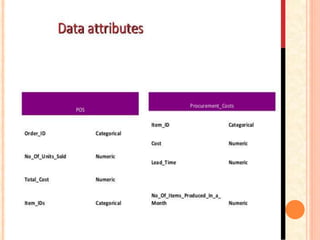
The document then lists several supply chain metrics and analytics tools, including warehouse management systems (WMS), transport management systems (TMS), enterprise resource planning (ERP), radio frequency identification (RFID), global positioning systems (GPS), and manufacturing execution systems (MES). It explains the purpose and frequency of measurement for each tool and lists the internal and external stakeholders.
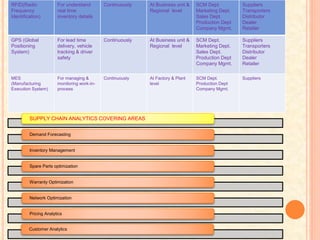
Finally, the document outlines areas of supply chain analytics like demand forecasting, inventory management