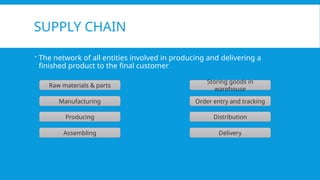
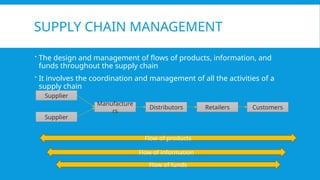
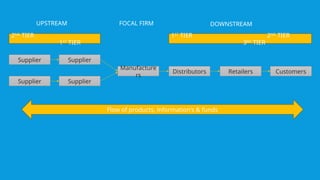
The document provides an overview of supply chain management, detailing its components, stages, and the importance of design in moving products from suppliers to customers. It emphasizes the role of big data in optimizing supply chain processes through predictive, descriptive, and prescriptive analytics, used for demand forecasting, risk management, and operational efficiency. Additionally, it highlights various internal and external data sources, along with examples of companies like Walmart, Amazon, and Unilever that effectively utilize analytics to enhance their supply chain operations.