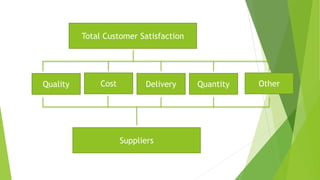
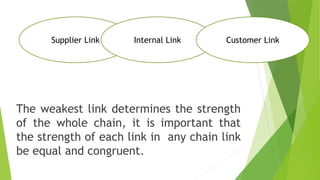
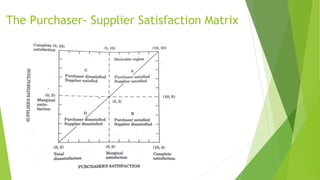
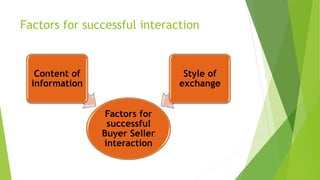
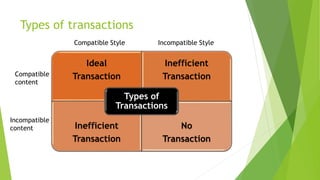
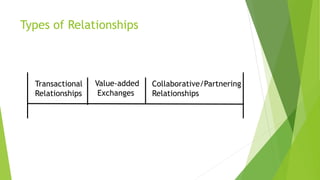
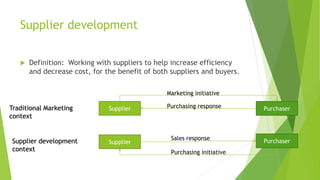
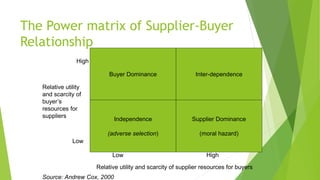
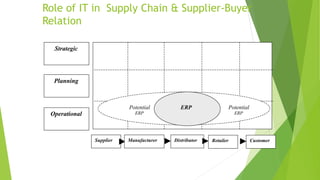
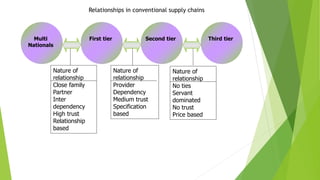
The document discusses various types of buyer-supplier relationships including transactional relationships, value-added exchanges, and collaborative/partnering relationships. It compares and contrasts transactional relationships with partnerships. Strategic alliances are defined as relationships based on mutual trust and open communication to reduce costs and improve quality. Supplier development aims to increase supplier efficiency through assistance. Effective buyer-supplier relationships require communication, trust, and a team approach. Relationship management also depends on internal team dynamics and understanding each party's goals.