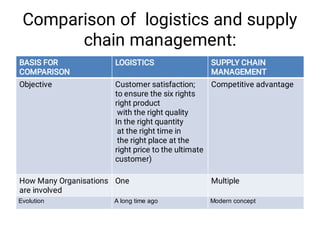
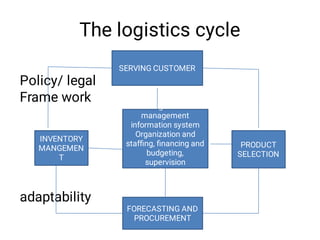
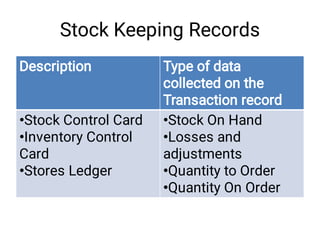
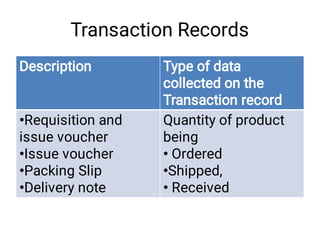
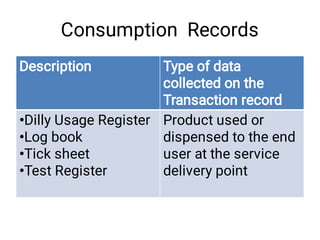
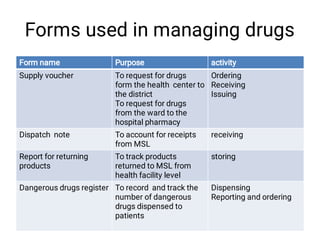
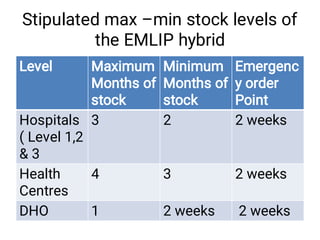
The document discusses supply chain management and logistics. It defines key terms like supply chain management, logistics, and the differences between the two. It also outlines the major activities in the logistics cycle including forecasting, procurement, inventory management, and key forms and records used like stock control cards and daily activity registers. Ordering processes, receiving, storage conditions and key performance indicators are also summarized.