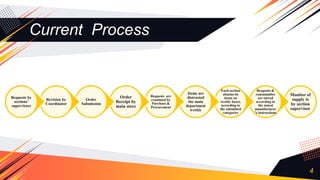
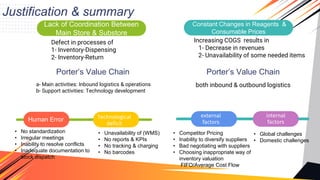
1. The document discusses two main challenges facing the supply chain of a hospital laboratory: lack of coordination between the main store and substores, and constant changes in reagent and consumable prices.
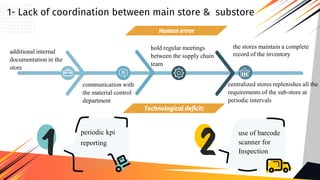
2. For the first challenge, contributing factors include human error, lack of standardization, and technological deficits like not having a warehouse management system. The solution involves improving documentation, communication, and implementing coordination mechanisms.
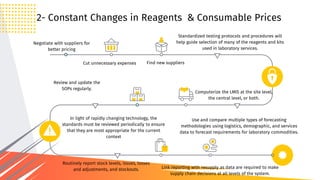
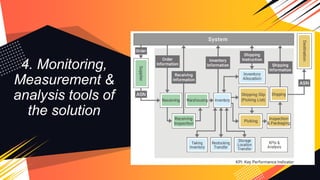
3. For the second challenge, both external factors like global supply issues and domestic inflation, and internal factors like pricing strategies contribute. Solutions center around forecasting, negotiating, updating procedures, and monitoring costs and inventory.