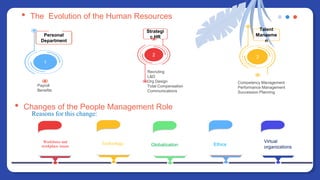
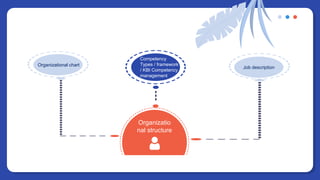
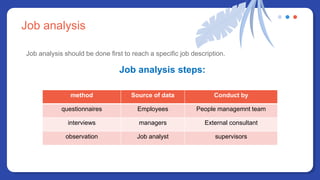
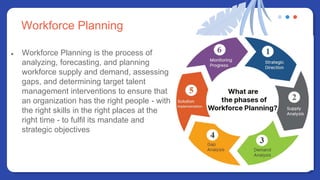
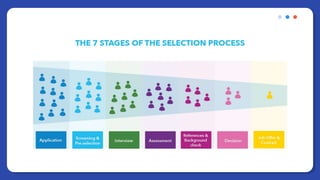
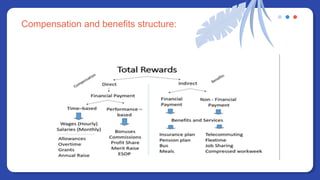
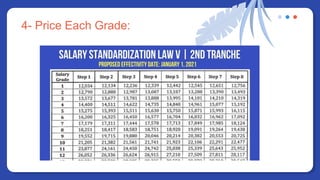
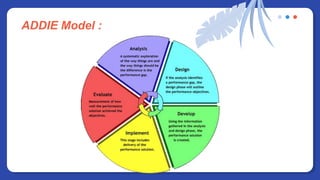
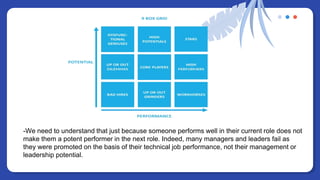
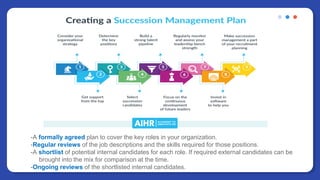
The document provides information on people management. It lists the names of 8 people in Group 1 and defines people management as the practices for managing an organization's human resources. It then discusses topics like the evolution of HR, changes to the people management role, workforce planning, sourcing candidates, the selection process, total rewards including compensation, building a pay structure, learning and development trends/challenges and the ADDIE model, talent management using a 9 box grid, and succession planning.