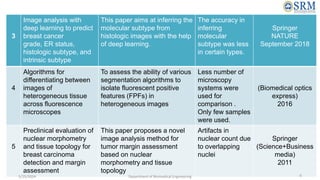
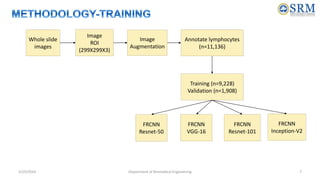
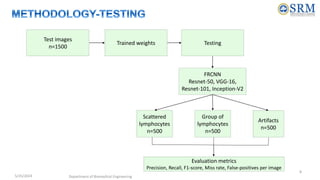
The document discusses a project aimed at automating the detection and counting of lymphocytes in immunohistochemistry images for cancer analysis using deep learning techniques. It highlights the importance of the immunoscore as a prognostic tool, alongside traditional cancer staging methods, in assessing patient survival rates. The project involves training a deep learning model and evaluates various image analysis methods to enhance accuracy in cancer prognosis.


![• Cancer is the result of mutations or abnormal changes in genes which are responsible
for controlling the growth of cells.
• Recurrence of cancer is one of the biggest issues in the field of oncology. Reasons for
recurrence depends on various factors such as cancer stage, genetic issues, histology,
treatments etc.
• Generally the recognized GOLD standard for cancer staging and prognosis is the TNM
staging system which provides an insight of the advancement of cancer in the body and
how far it has spread.
• Based on this, treatment is administered to patients for their recovery and for prevention
of recurrence of cancer.
• Apart from this, recently a new parameter has been considered to play a major role in
assessing the survival rate of patients called as the Immunoscore. This parameter
contributes up to 47% of the survival rate [1].
[1] Franck Pagès et al, “International validation of the consensus Immunoscore for the classification of colon cancer: a prognostic and accuracy study”- Lancet (2018) 391:
2128–39
25-05-2024 Department of Biomedical Engineering 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/secondreviewresearch-240525112955-1d053a8f/85/Second-Review-Research-in-quantifying-lymphocytes-pptx-3-320.jpg)


![[1] Franck Pagès et al, “International validation of the consensus Immunoscore for the classification of colon cancer: a prognostic and accuracy study”- Lancet (2018)
391: 2128–39.
[2] Leonid Kostrykin et al, “Segmentation of cell nuclei using intensity-based model fitting and sequential convex programming”- IEEE 15th International Symposium on
Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) (2018) 978-1-5386-3636-7/18.
[3] Rhea Chitalia et al, “Algorithms for differentiating between images of heterogeneous tissue across fluorescence microscopes ”- Biomedical optics express (2016) Vol.
7, No. 9.
[4] Jun Kong et al, “Automated cell segmentation with 3D fluorescence microscopy images”- IEEE (2015) 978-1-4799-2374-8/15.
[5] Ndeke Nyirenda, Daniel L. Farkas, and V. Krishnan Ramanujan, “Preclinical evaluation of nuclear morphometry and tissue topology for breast carcinoma detection
and margin assessment”- Springer Science+Business Media (2011) 126(2): 345–354.
[6] Jenna L. Mueller et al, “Quantitative Segmentation of Fluorescence Microscopy Images of Heterogeneous Tissue: Application to the Detection of Residual Disease in
Tumor Margins”- PLOS ONE(2013) Volume 8, Issue 6.
[7] Kaustav Nandy et al, “Automatic Segmentation and Supervised Learning Based Selection of Nuclei in Cancer Tissue Images”- Cytometry Part A (2012) 81A:743–754.
[8] Alexandre Dufour et al, “Segmenting and Tracking Fluorescent Cells in Dynamic 3-D Microscopy With Coupled Active Surfaces ”- IEEE Transactions on image
processing (2005), Vol. 14, No. 9.
[9] Jeroen A.M. Belie¨n et al, “Confocal DNA Cytometry: A Contour-Based Segmentation Algorithm for Automated Three-Dimensional Image Segmentation”- Cytometry
(2002) 49:12–21.
[10] Gang Lin et al, “A Multi-Model Approach to Simultaneous Segmentation and Classification of Heterogeneous Populations of Cell Nuclei in 3D Confocal Microscope”-
Cytometry Part A (2007) 71A: 724736 .
[11] Umesh Adiga et al, “High-Throughput Analysis of Multispectral Images of Breast Cancer Tissue”- IEEE Transactions on image processing (2006), Vol. 15, No. 8.
[12] Umesh Adiga et al, “Characterization and automatic counting of F.I.S.H. signals in 3-D tissue images”-Image Anal Stereol(2001) 20:41-52.
[13] Shekar singh et al, “Breast cancer detection and classification of histopathological images”-International journal of engineering science and technology (2011) Vol. 3,
No. 5.
[14] Munezza Ata Khan et al, “Detection and Characterization of Antinuclear Antibody using fluorescence image processing”- IEEE International Conference on Robotics
and Emerging Allied Technologies in engineering (2014) 978-1-4799-5132-1/14
[15] Michael J. Sanderson et al, “Fluorescence Microscopy”-Cold Spring Harb Protoc. (2016) (10)
25-05-2024 Department of Biomedical Engineering 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/secondreviewresearch-240525112955-1d053a8f/85/Second-Review-Research-in-quantifying-lymphocytes-pptx-9-320.jpg)
