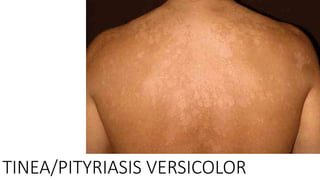
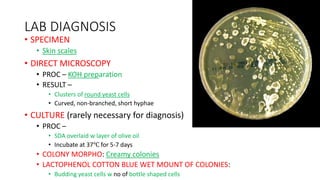
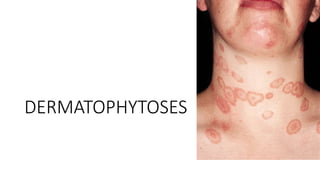
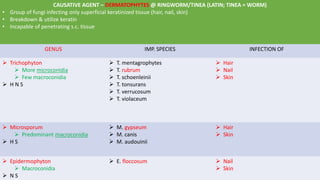
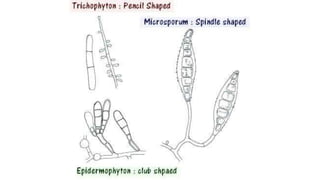
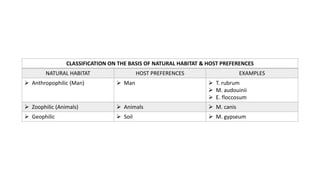
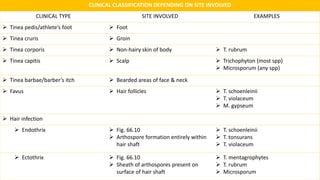
This document discusses classification of fungal diseases, including superficial and deep mycoses. Superficial mycoses are strictly skin infections, including tinea versicolor caused by Pityrosporum orbiculare. Dermatophytoses are fungal infections of the skin, hair, and nails caused by dermatophytes like Trichophyton and Microsporum. Clinical classification depends on site involved, such as tinea pedis of the foot. Laboratory diagnosis involves direct microscopy of skin/hair/nail samples in KOH to view fungal hyphae, and culturing samples on SDA to identify dermatophytes based on morphology and microscopy of microconidia and macroconidia