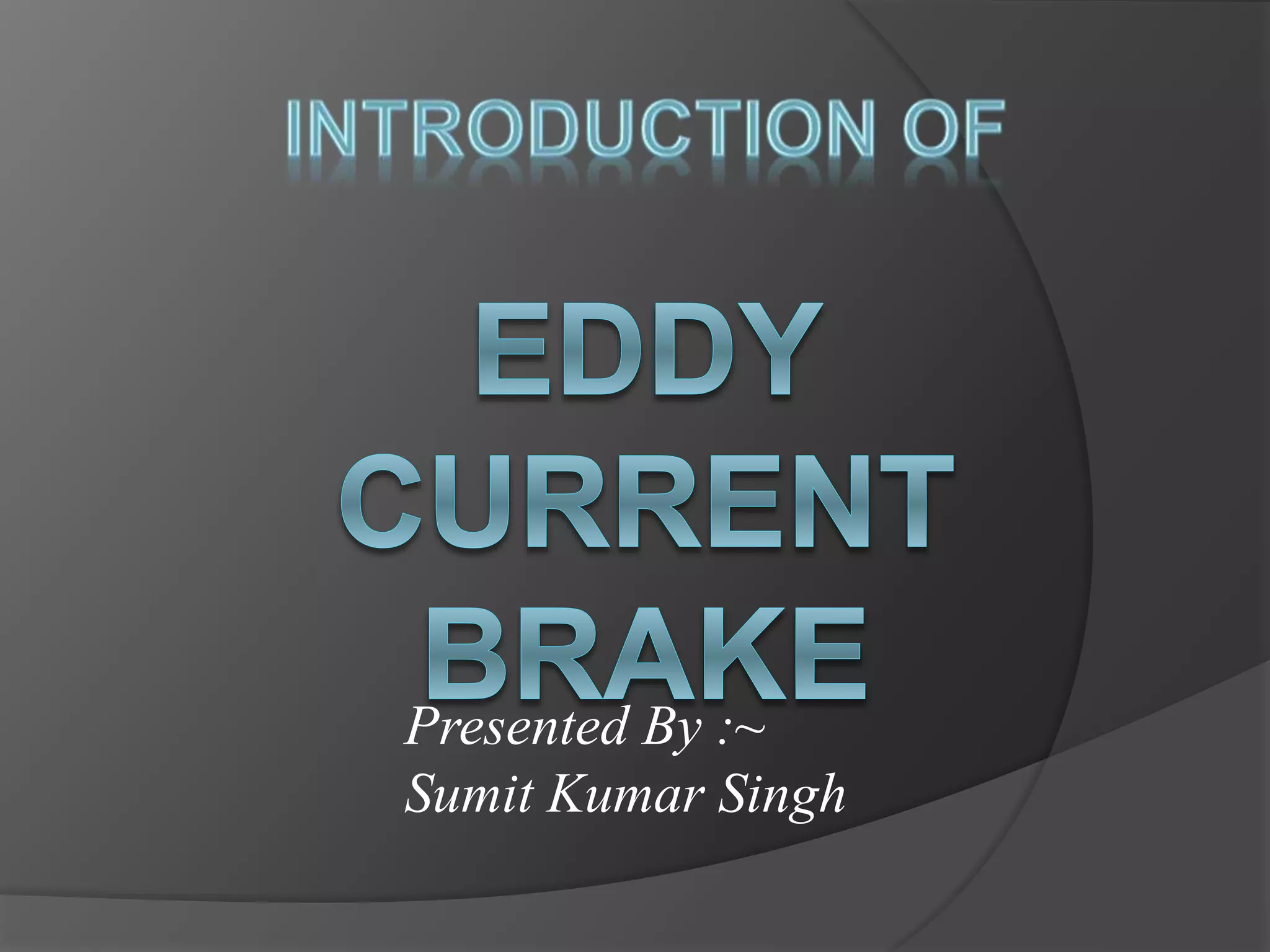
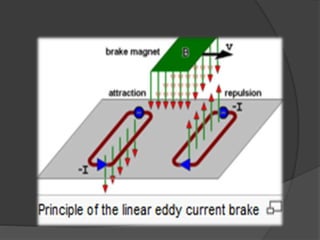
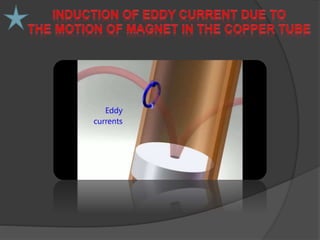
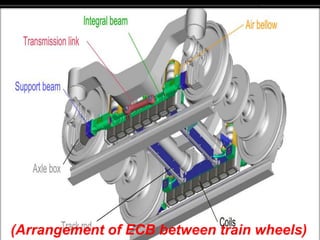
The document discusses eddy current brakes, which use magnetic fields to induce eddy currents in conductors to slow rotation or movement. There are two types - circular brakes use a disc that generates eddy currents when exposed to a magnetic field, while linear brakes induce currents in rails using a magnet held near the rail. Eddy current brakes have advantages like contactless braking and adjustable braking force, but cannot hold stationary loads. They are used in trains and rollercoasters for safety braking at high speeds. Future applications could replace ordinary brakes and control high speed trains entirely with eddy current brakes.