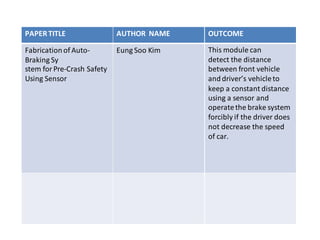
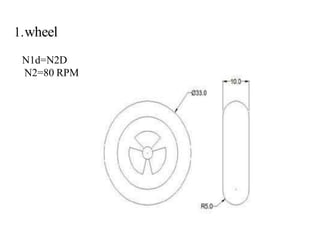
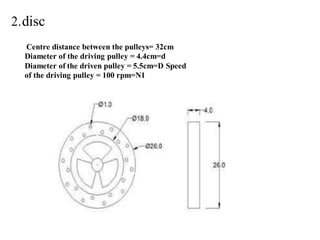
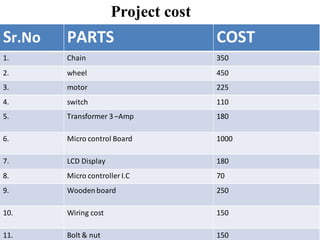
This document describes the design and development of an electromagnetic and automatic braking system. It provides an introduction to the project, lists the main components used including discs, DC motors, electromagnets and sensors. It discusses the working principle of eddy currents in electromagnetic braking. The document reviews previous literature on related braking systems and outlines the types of brakes. It also includes the construction, advantages and applications of the system as well as a proposed methodology and references.