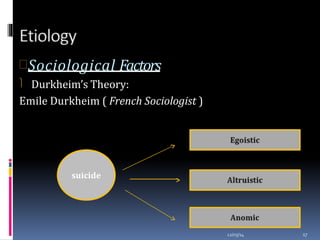
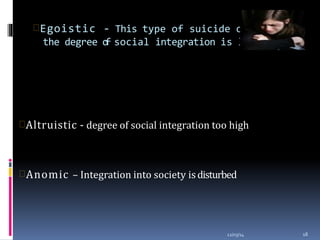
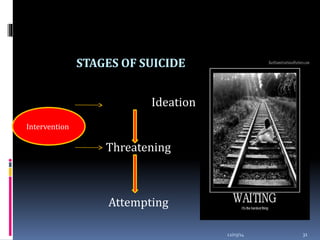
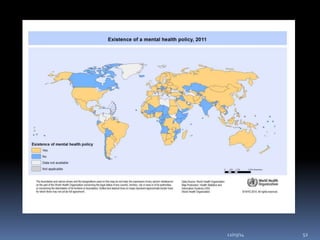
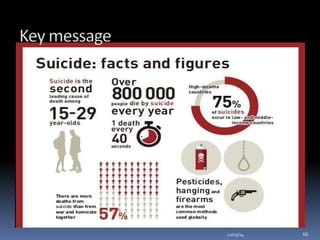
This document discusses suicide from various perspectives including definitions, global and historical context, risk and protective factors, methods, stages, warning signs, treatment, and prevention recommendations. It covers sociological, psychological, and biological theories of suicide etiology. High-risk groups are identified as those with psychiatric disorders, the elderly, prior attempters, and occupational groups with access to lethal means. Prevention strategies proposed include population-level public awareness/education, restricting access to means, screening and treatment of high-risk groups, and training gatekeepers such as health professionals to identify individuals with warning signs.