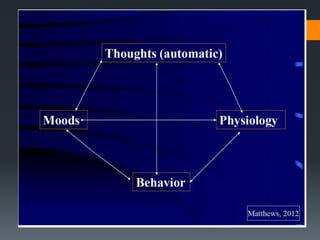
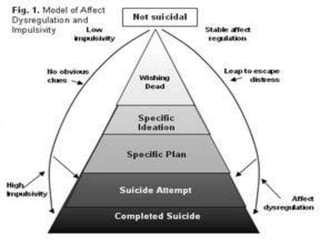
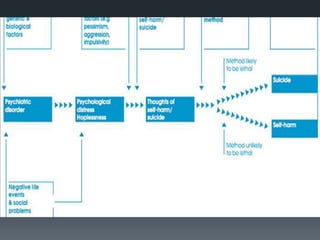
The document discusses suicidal patients and suicide risk assessment. It outlines several factors that contribute to the development of suicidal crises, including perceiving problems as unsolvable and believing death will bring relief. Suicidal individuals often feel hopeless about enduring or solving their difficulties. Those at higher risk include those with psychiatric disorders, life stressors, physical illness, personality disorders or social problems. A comprehensive assessment evaluates demographics, life stressors, diagnoses, and family history of suicide. Feelings of hopelessness and helplessness are also assessed. Treatment includes crisis intervention, focusing on preventing suicide through assessment and identifying high-risk individuals, as well as continuing therapy viewing suicidality as a problem behavior to address.