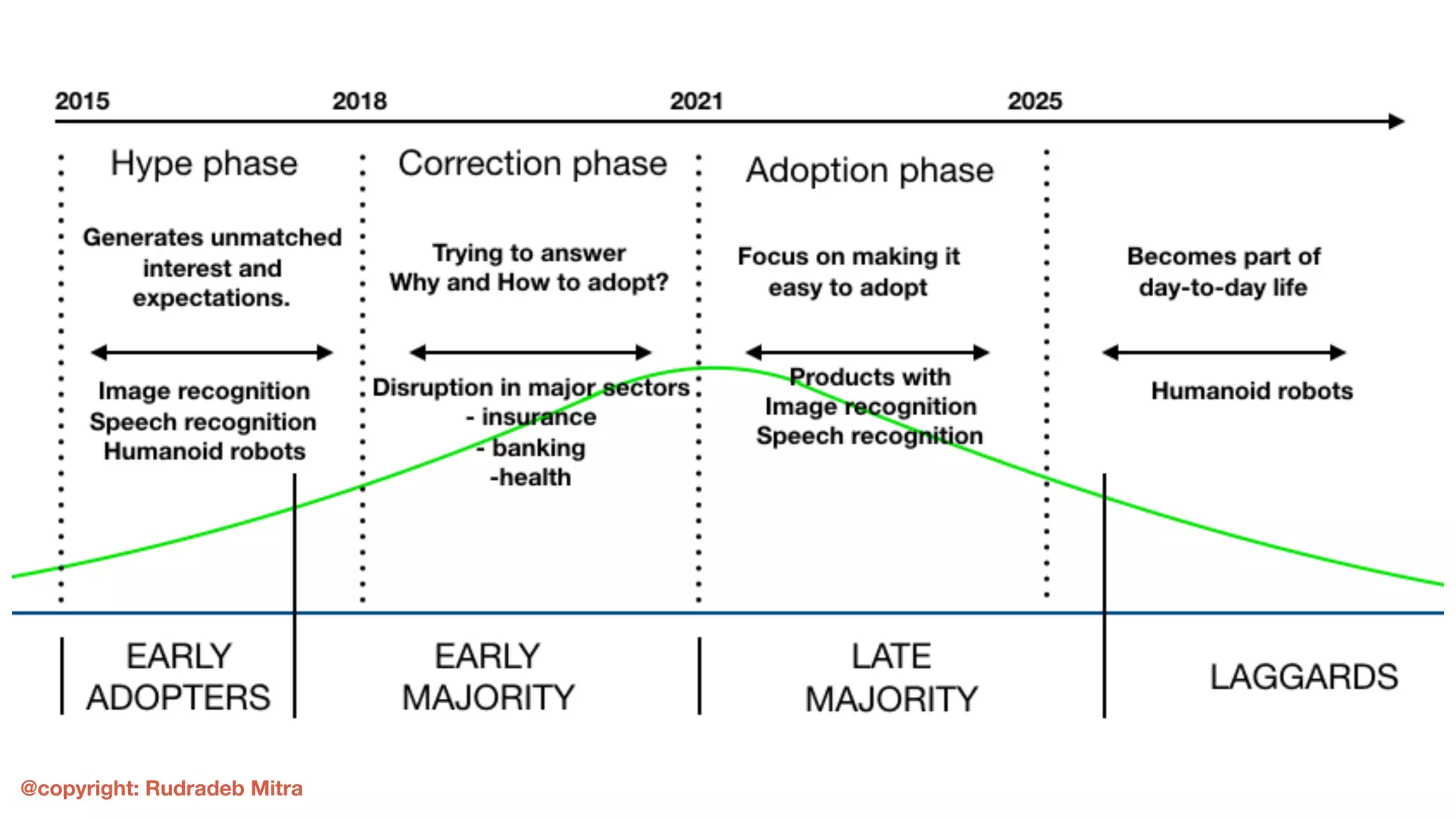
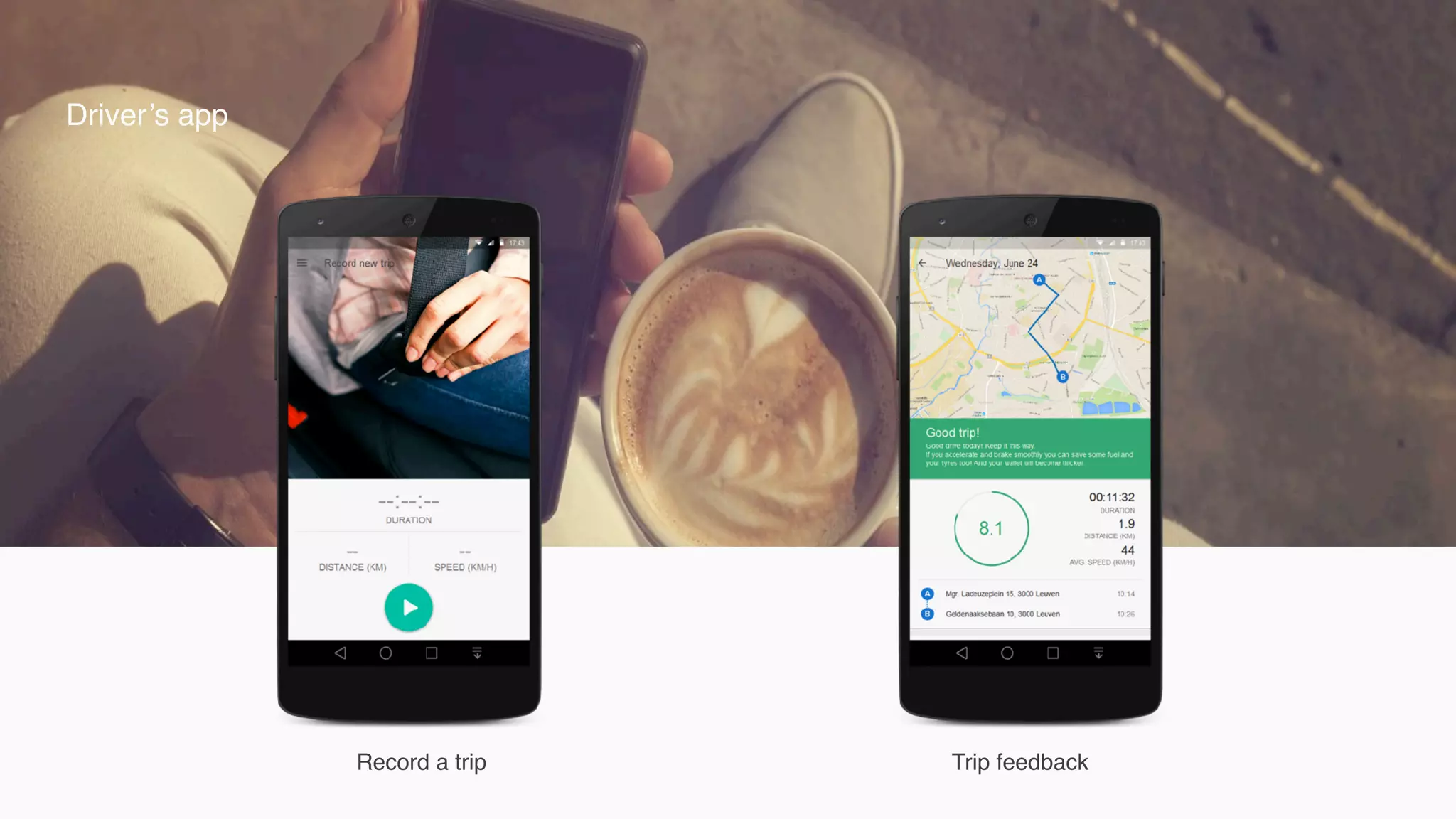
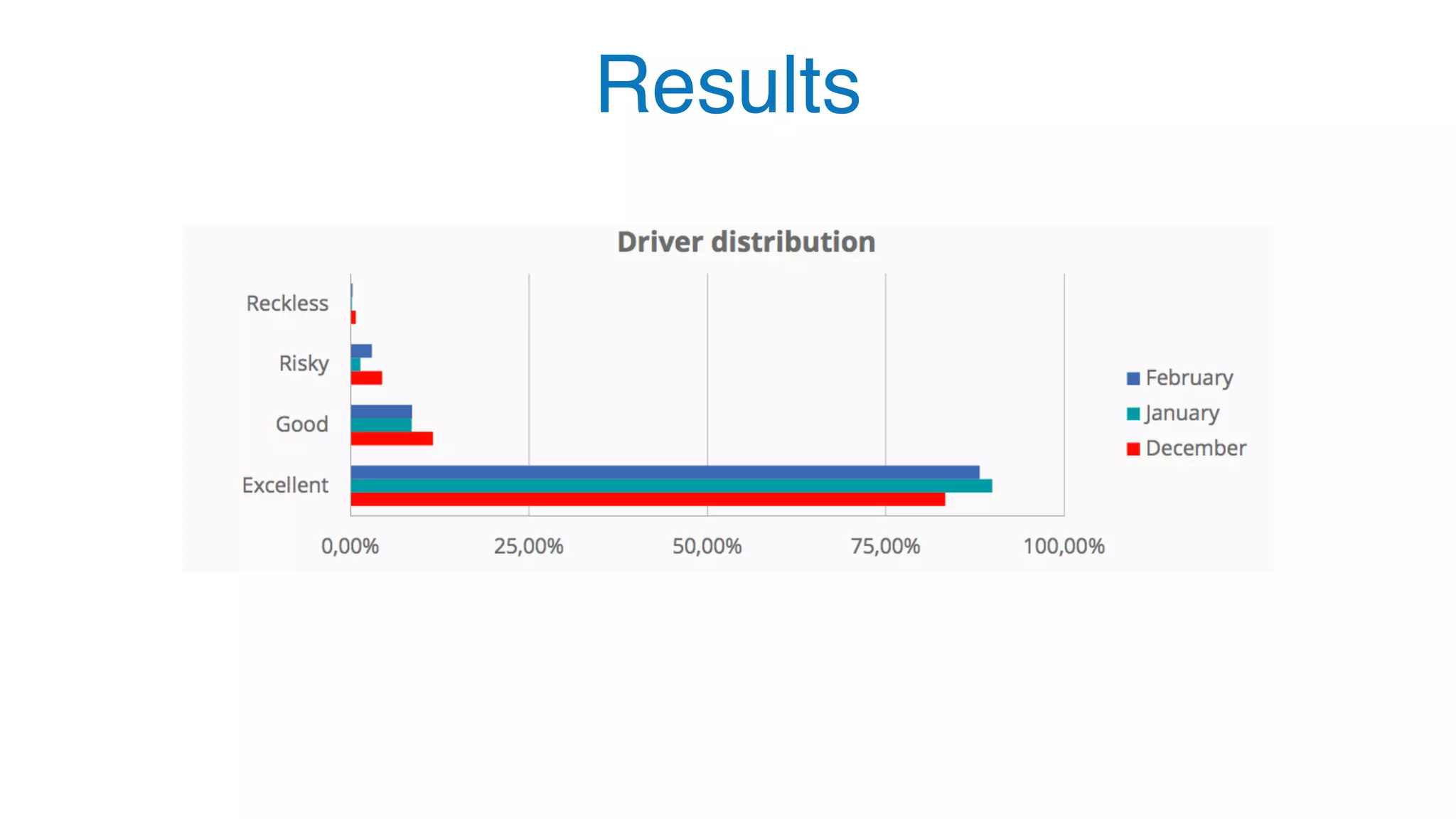
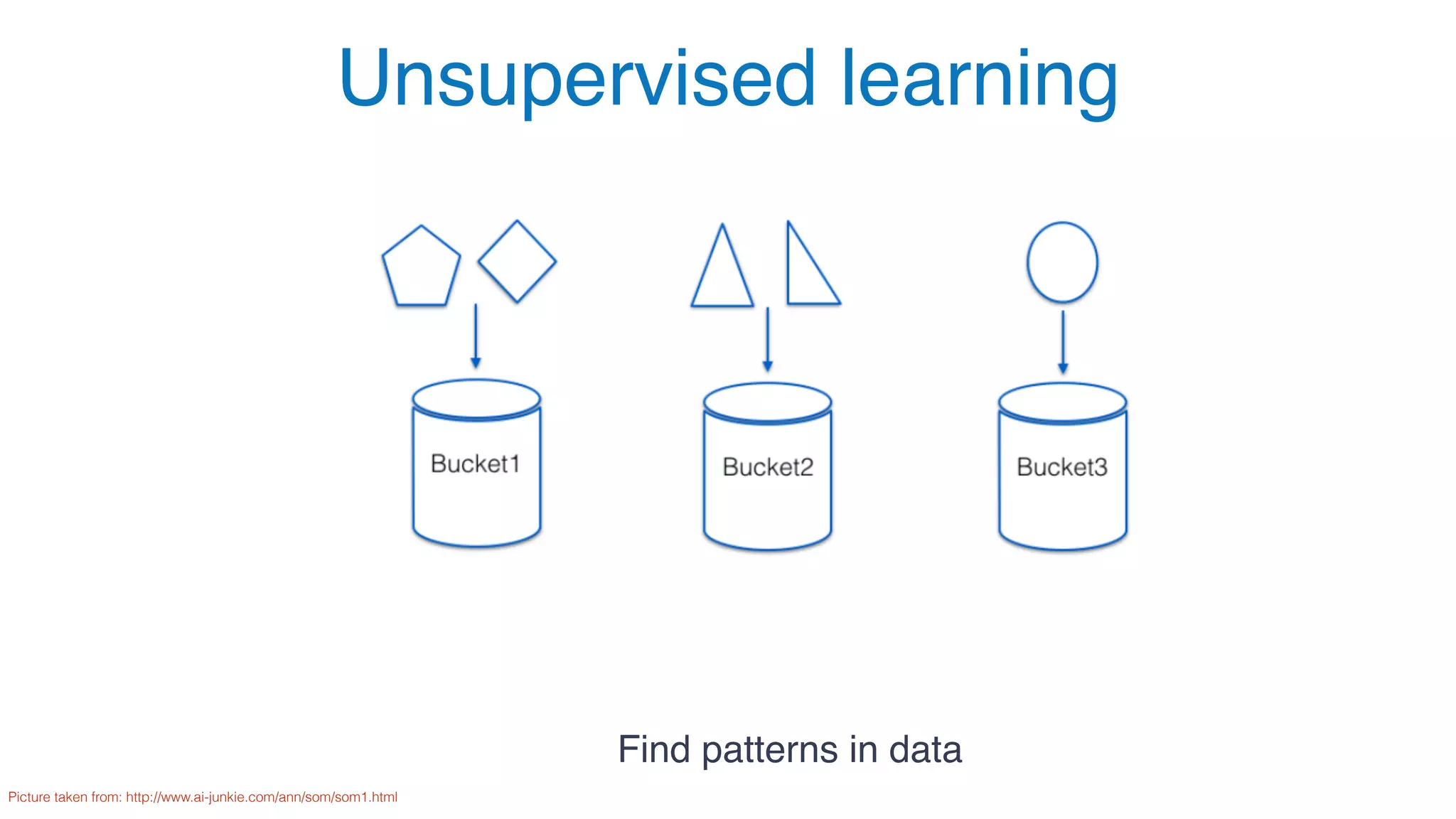
The document outlines the process for successfully adopting machine learning, emphasizing the importance of selecting the right problem to solve and the different types of learning algorithms. It provides case studies illustrating challenges in areas like insurance for young drivers, decentralized energy via solar rooftop, and providing loans to the unbanked, highlighting the data collection and algorithm selection challenges faced. Ultimately, it stresses that users must be incentivized to share data for effective machine learning product development.