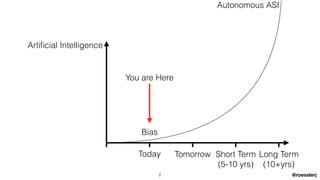
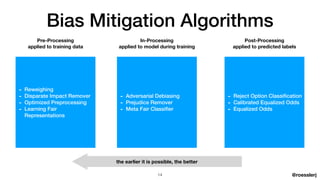
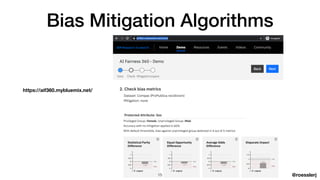
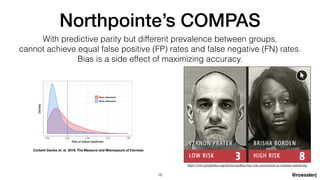
Dr. Jeremias Rößler's document discusses biases in artificial intelligence, particularly focusing on algorithmic and statistical biases and their implications in various applications, such as criminal sentencing. It emphasizes the challenges of achieving fairness in AI systems, highlighting the conflict between different definitions of fairness and the ethical considerations that arise from these biases. The document also outlines several bias mitigation strategies and stresses the importance of context in addressing bias within AI technologies.