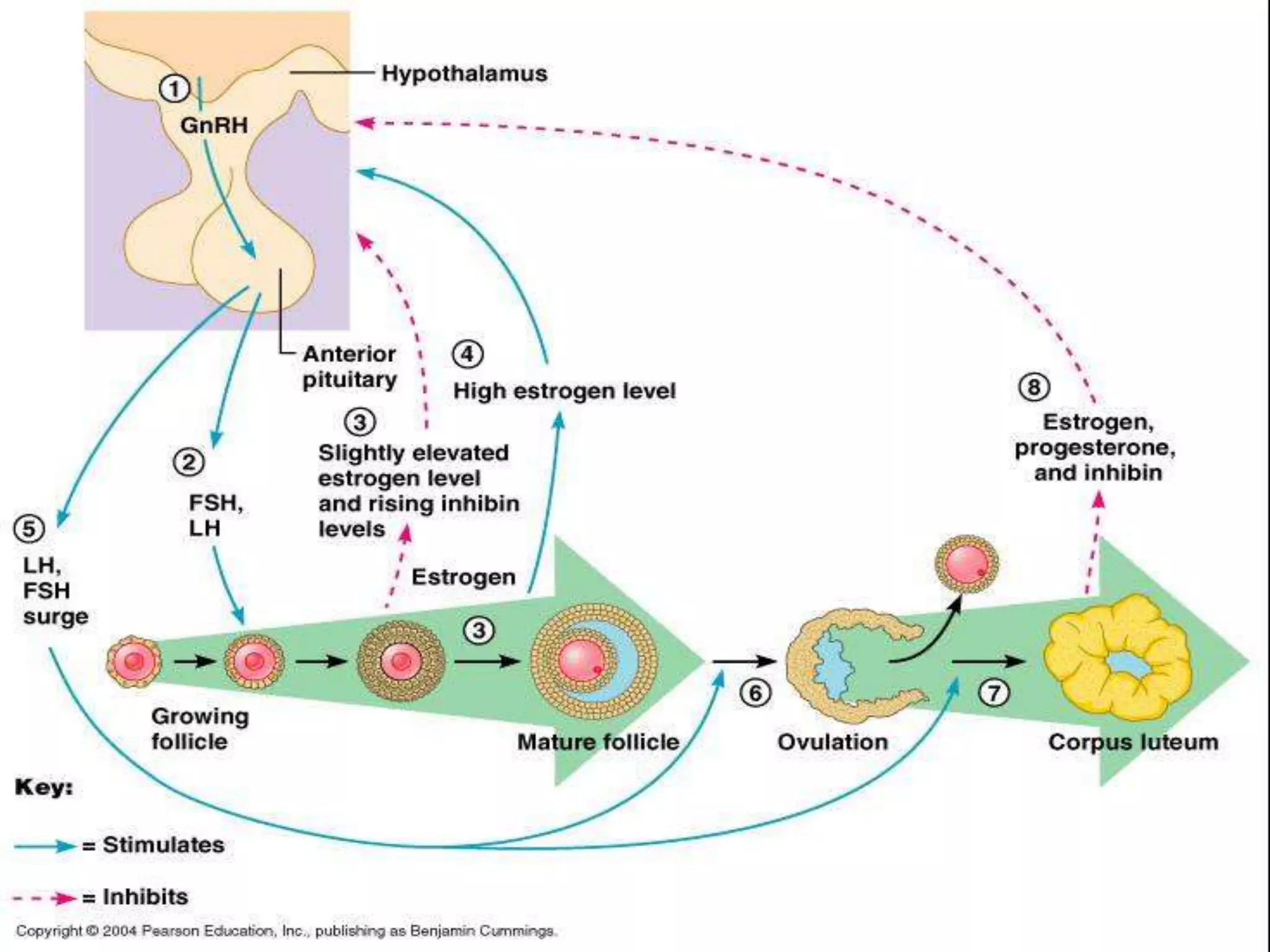
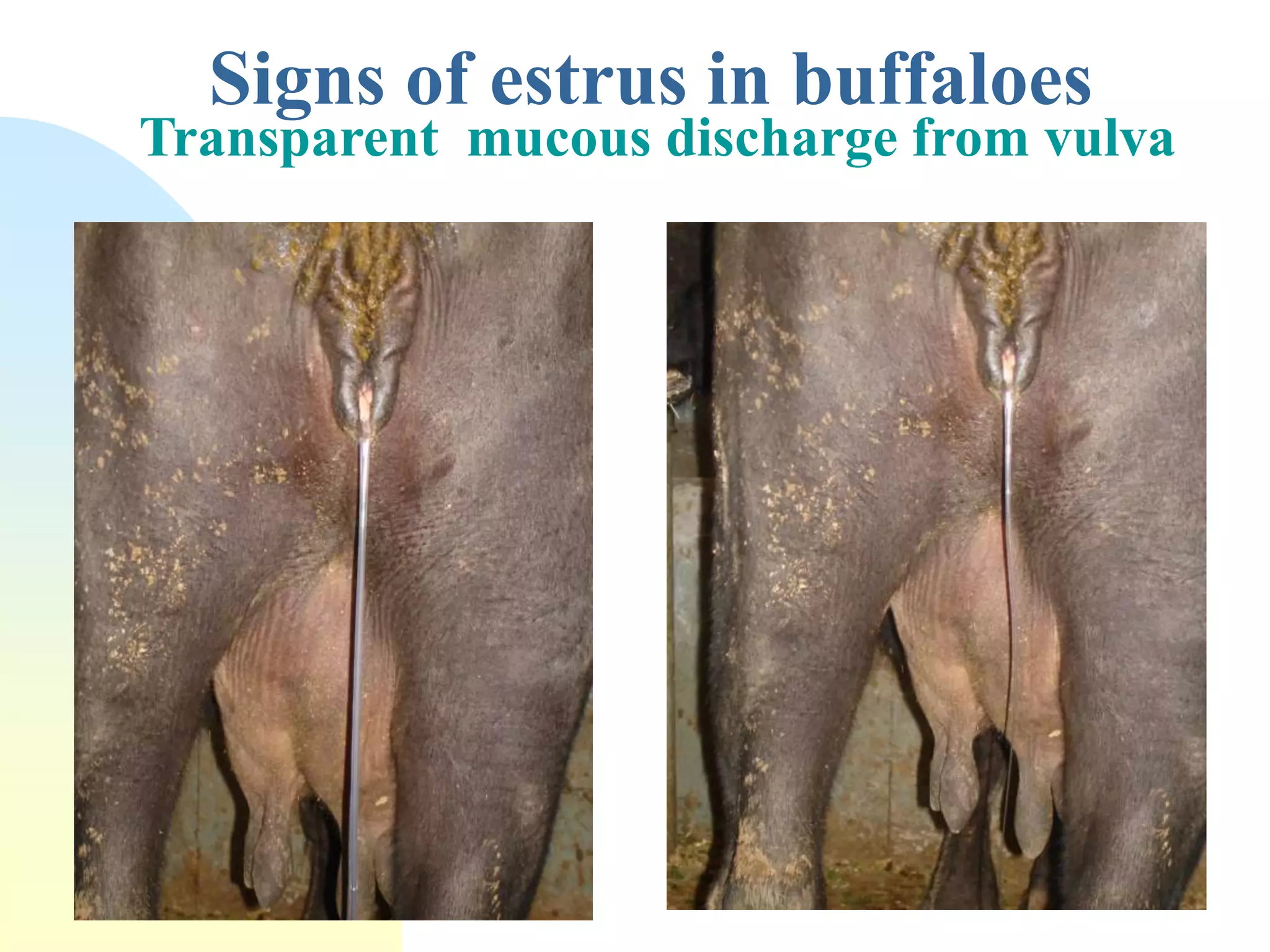
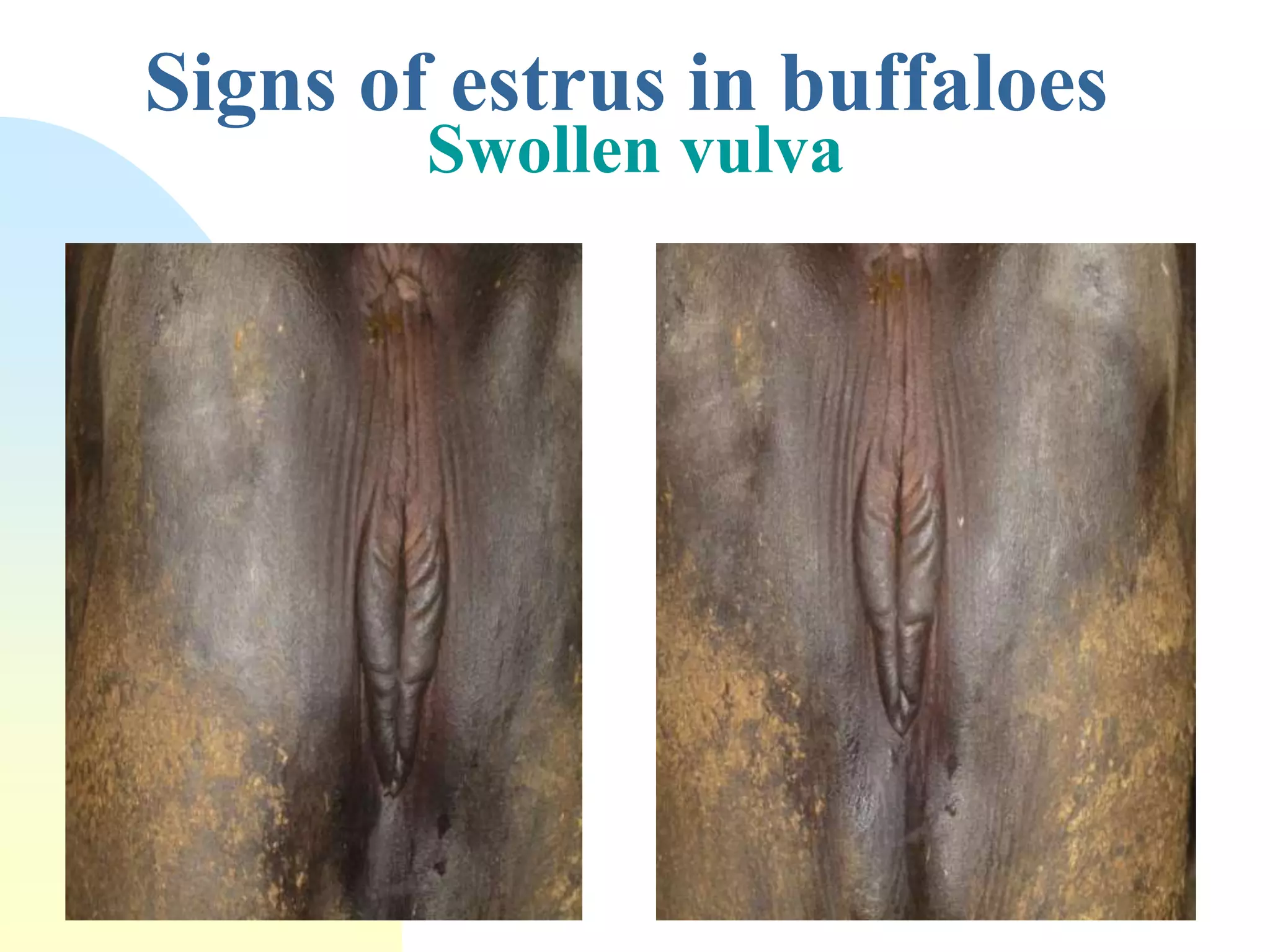
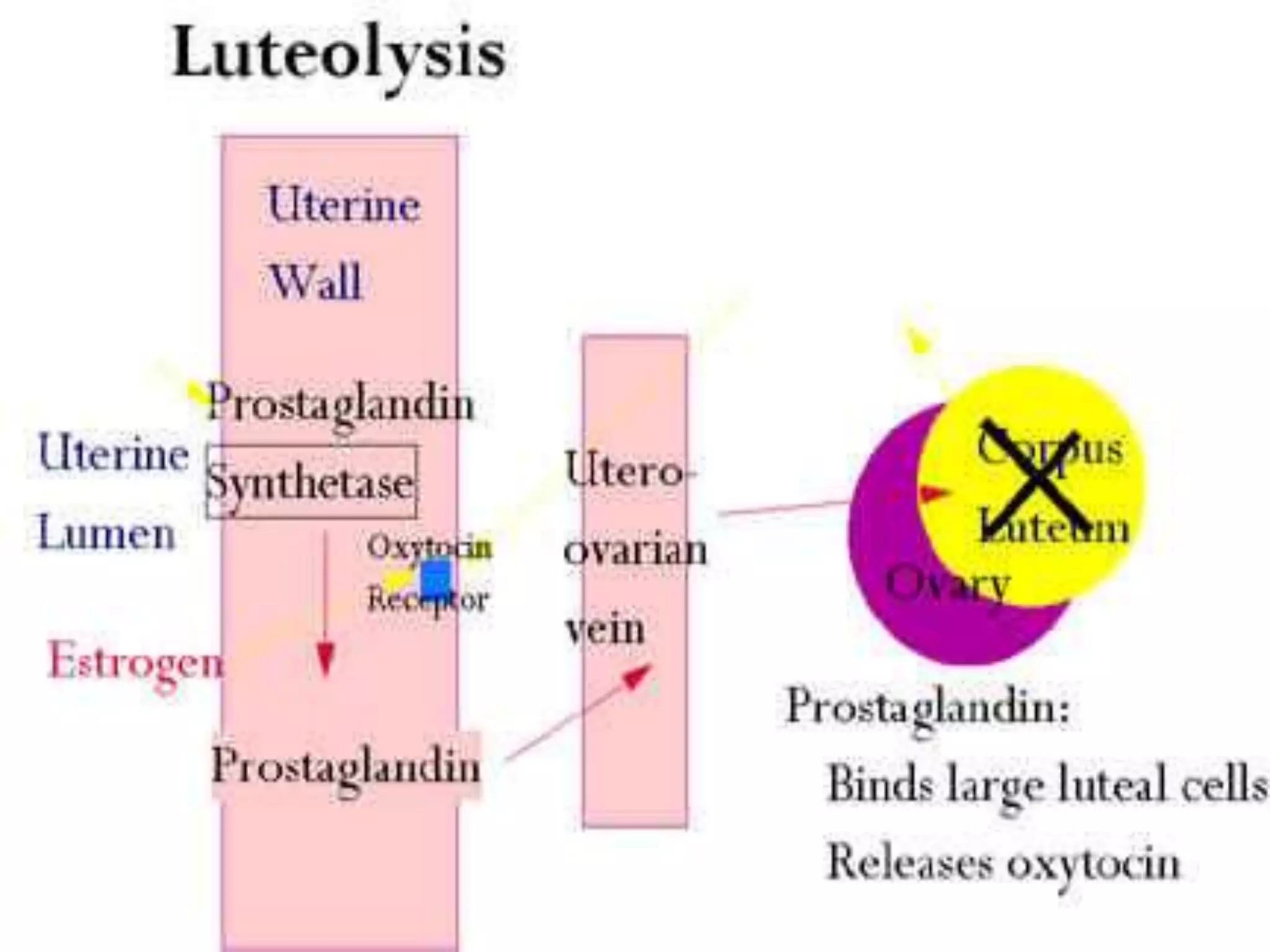
The document discusses the estrus cycle in buffaloes, detailing its phases, signs of heat, and factors influencing the cycle. Buffaloes reach puberty between 36 to 42 months with a heat duration of 12-24 hours and an estrus cycle length of 21 days. Silent heat is identified as a major challenge for breeding, often occurring in hot seasons, and requires combined detection methods for efficient identification.