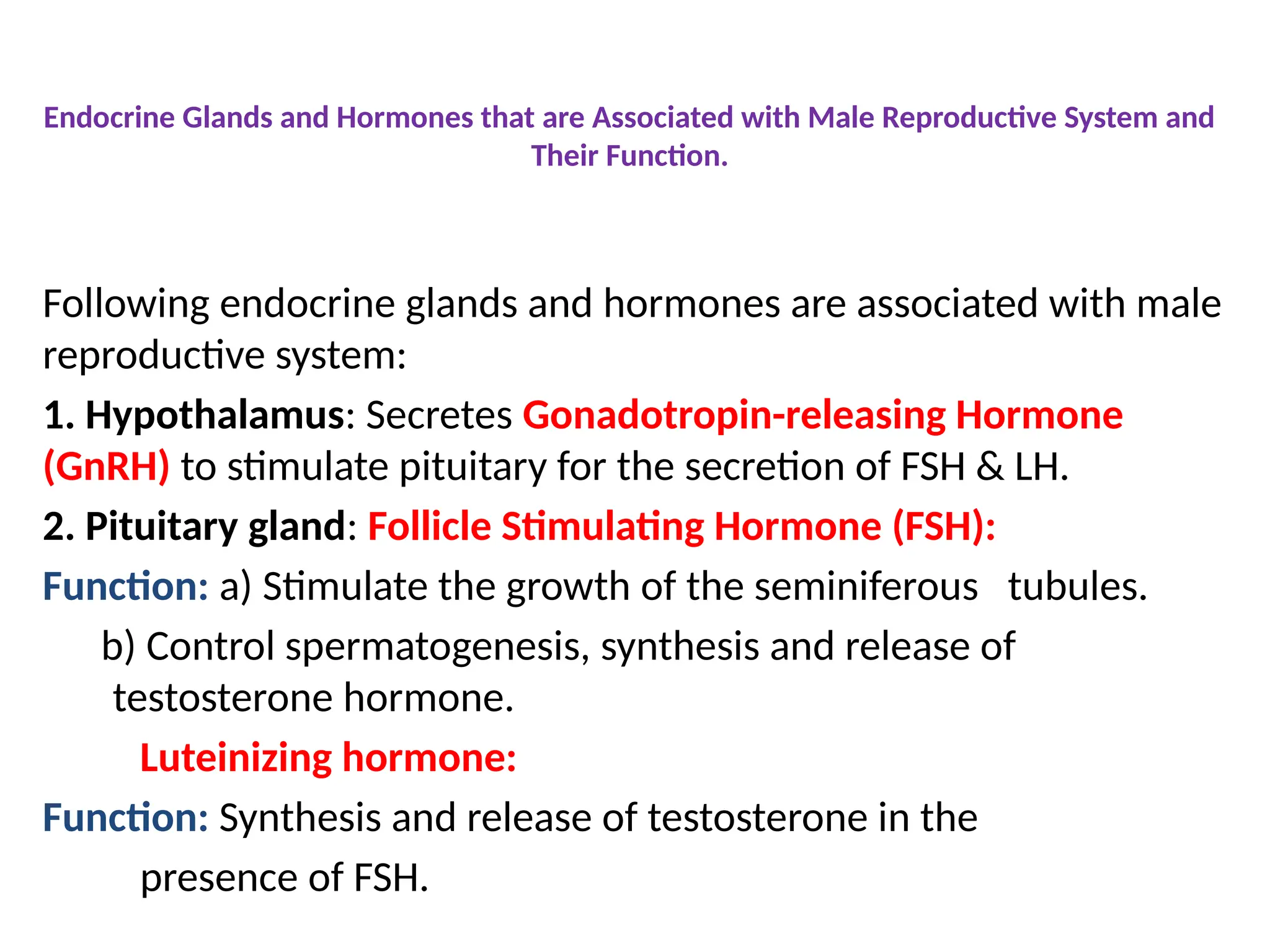
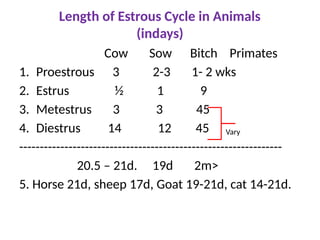
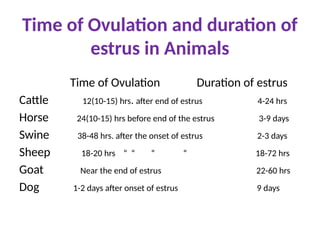
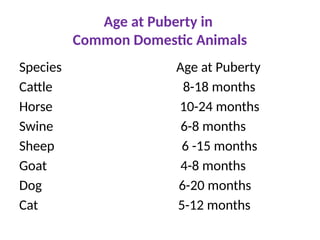
The document details the endocrine glands and hormones associated with the male and female reproductive systems, outlining their functions and interactions. Key components include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, ovaries, testes, and their hormonal influences like testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone. It also describes the estrous cycle in animals and the menstrual cycle in primates, explaining various phases and associated physiological changes.