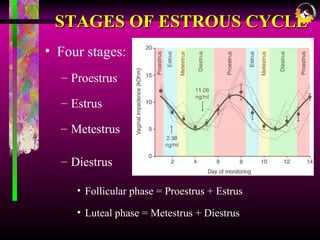
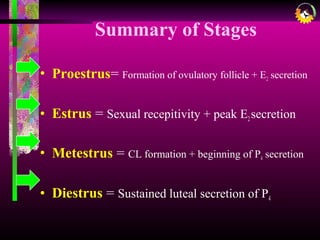
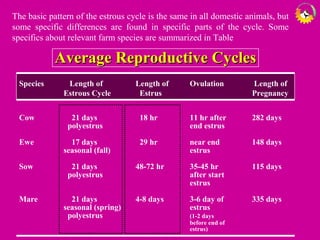
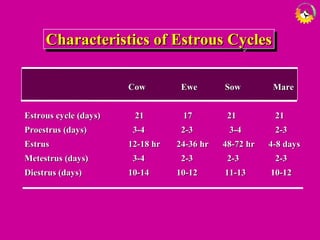
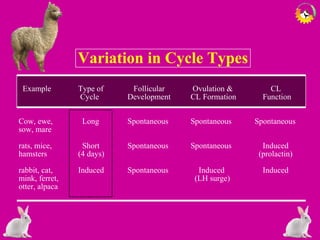
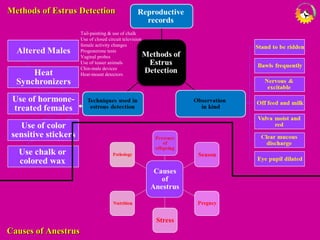
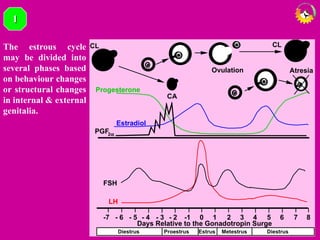
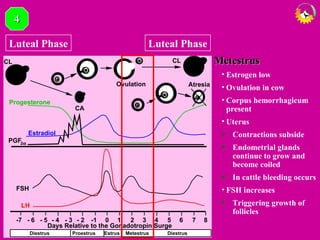
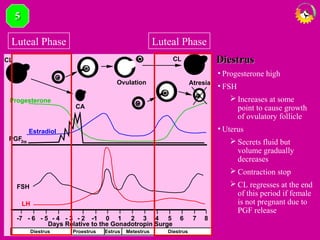
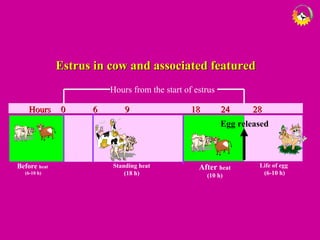
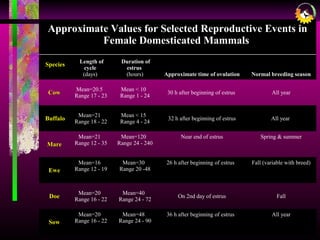
The document details the estrous cycle in female mammals, outlining its phases: follicular and luteal, along with the stages of proestrus, estrus, metestrus, and diestrus. It discusses variations among species, such as polyestrous, seasonal polyestrous, and monoestrous cycles, and highlights hormone levels during different phases. Additionally, it provides reproductive cycle characteristics for several domestic species, emphasizing the importance of hormonal regulation and physical changes in the reproductive tract.