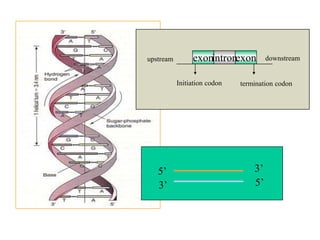
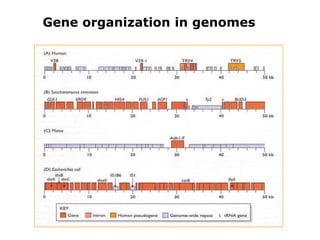
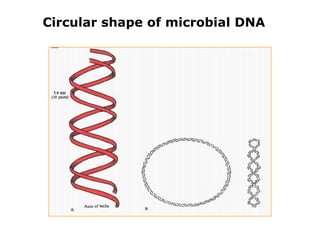
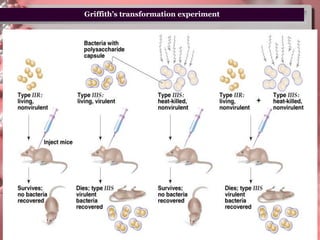
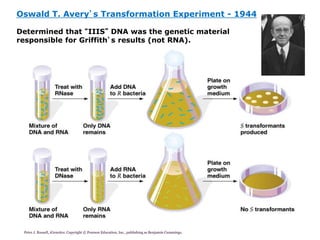
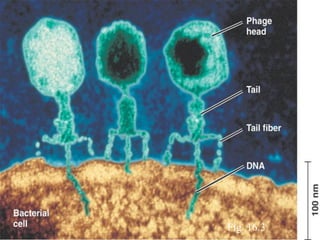
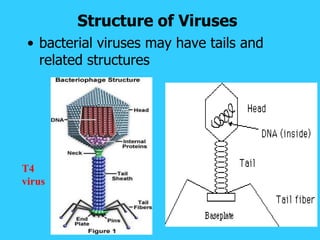
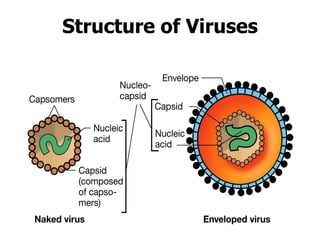
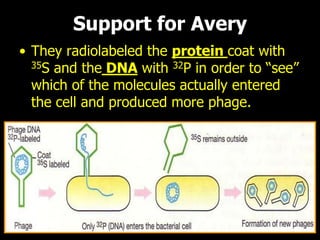
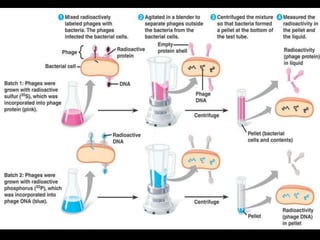
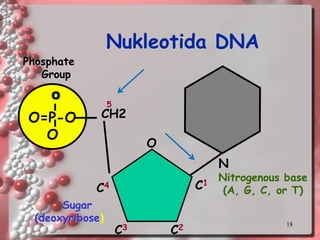
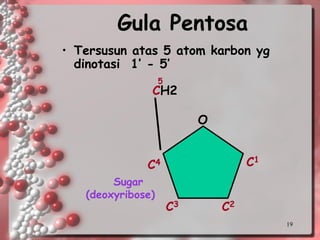
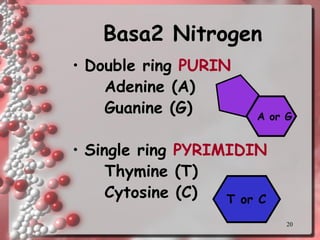
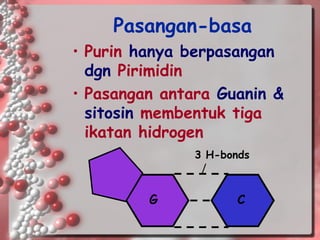
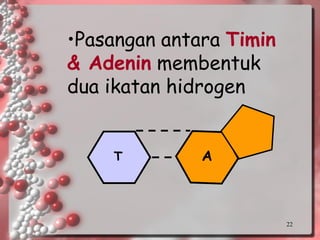
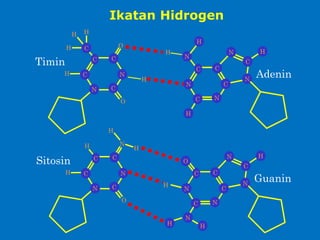
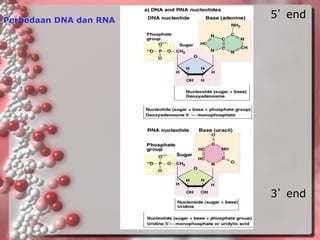
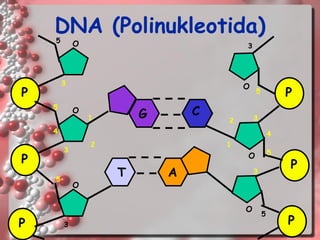
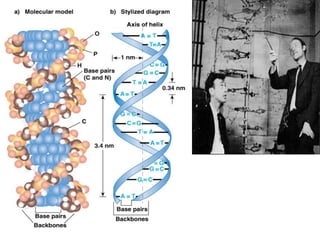
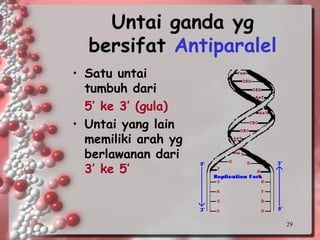
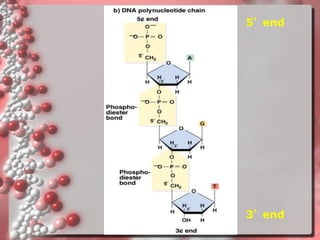
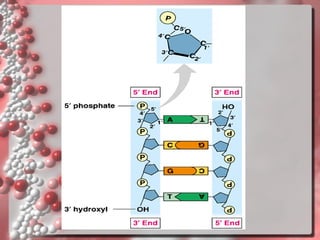
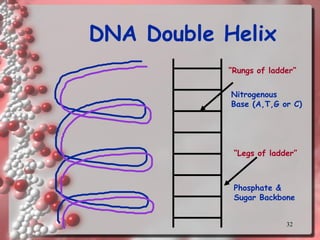
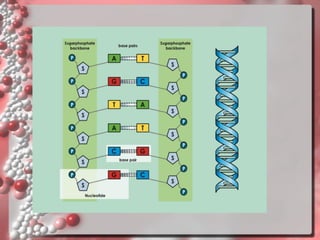
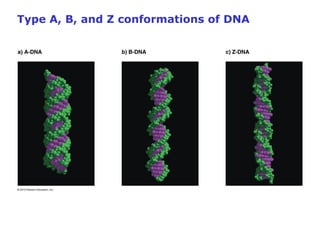
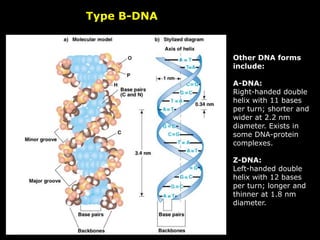
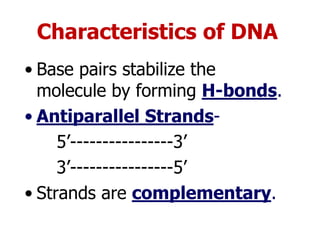
DNA is the genetic material found in living organisms. It is a polymer made up of nucleotides that stores and transmits genetic information. Griffith's transformation experiment showed that DNA is the genetic material by demonstrating that non-virulent bacteria could become virulent after uptake of DNA from dead virulent bacteria. Further experiments by Avery, Hershey and Chase provided stronger evidence that DNA, not proteins, was the genetic material. The double-helix structure of DNA was discovered by Watson and Crick based on Rosalind Franklin's X-ray crystallography data, with the two strands running in opposite directions and connected through complementary base pairing.















![Two types of organism:
Eukaryotes;
cells contain membrane-bound
compartments, including a nucleus and organelles.
Eukaryotes include: animals, plants, fungi, and
protozoa.
Prokaryotes:Lack internal compartments extensively.
Divided into two groups: bacteria and archaea.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strukturdna-140913105945-phpapp01/85/Struktur-dna-40-320.jpg)