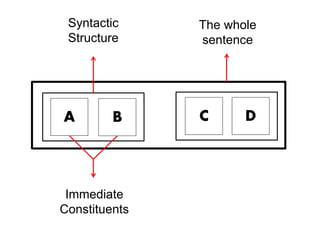
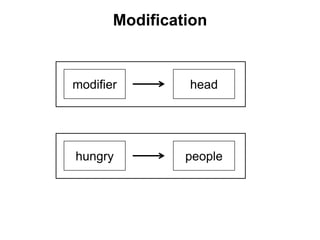
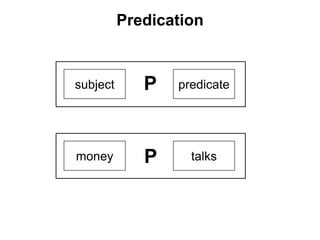
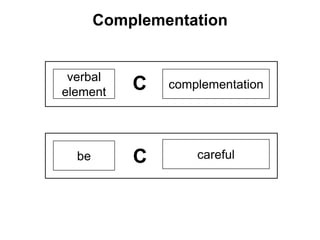
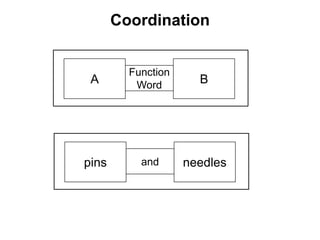
The document discusses Leonard Bloomfield's immediate constituent theory, which posits that structures can be divided into immediate constituents, often resulting in two branches that can be further subdivided to reach ultimate constituents (words). It outlines various syntactic structures, including modification, predication, complementation, and coordination, with examples illustrating these structures. Additionally, it explores the usage of subjects in different contexts, including pronouns, prepositional phrases, and temporary subjects.