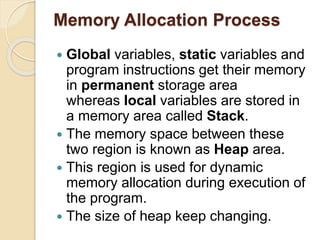
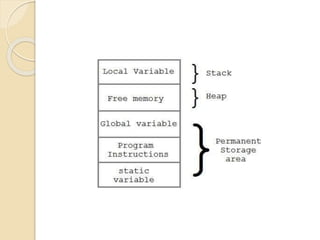
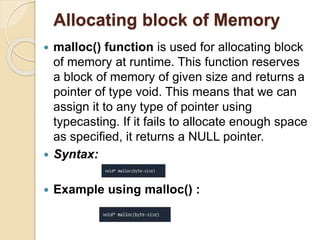
Dynamic memory allocation refers to the process of allocating memory at runtime using memory management functions defined in stdlib.h, which includes functions like malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), and free(). It contrasts with static memory allocation where global and static variables occupy permanent storage, while local variables reside on the stack and dynamic memory is allocated from a changing heap area. Proper memory management is essential, as failing to release memory with free() can lead to memory consumption until program termination.