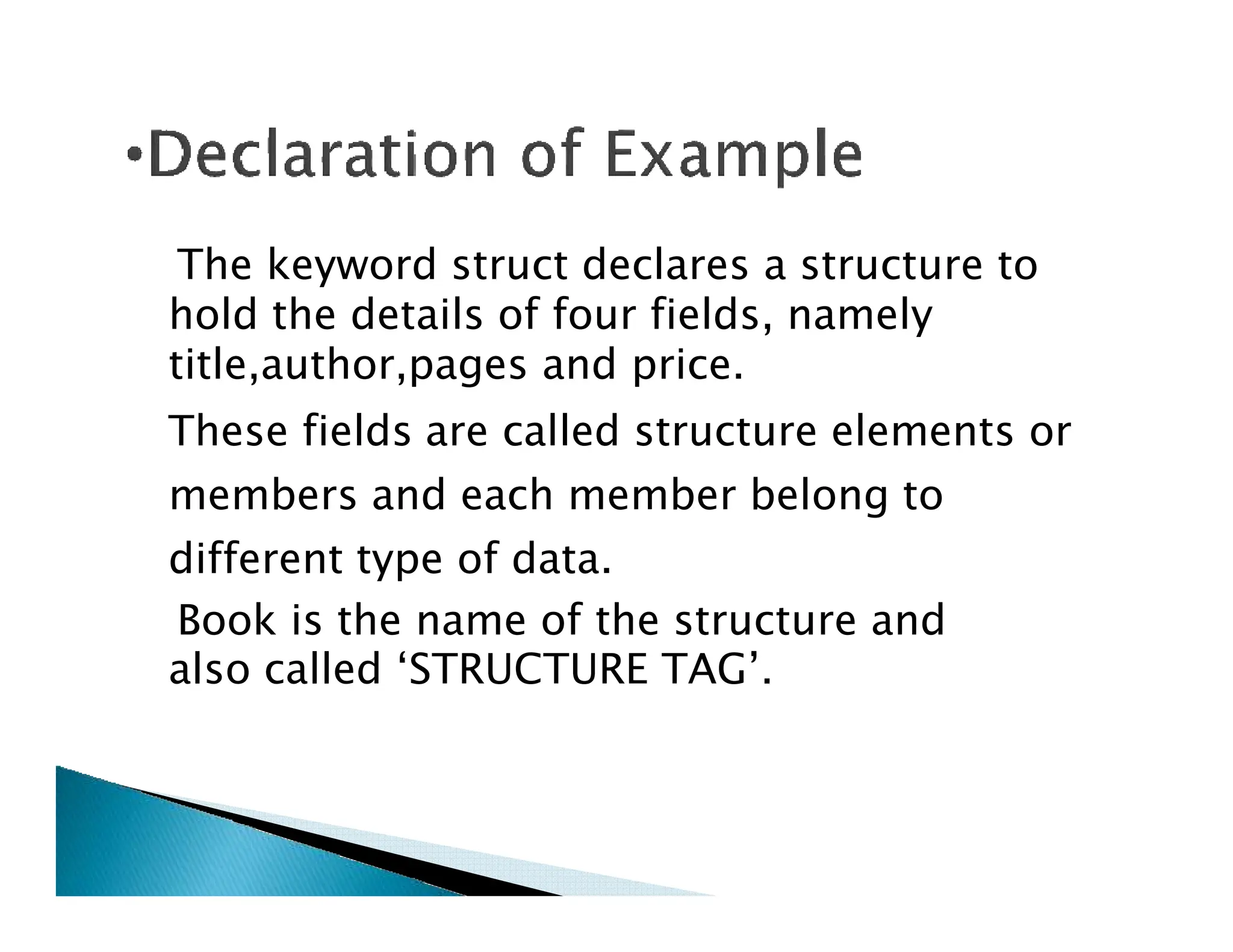
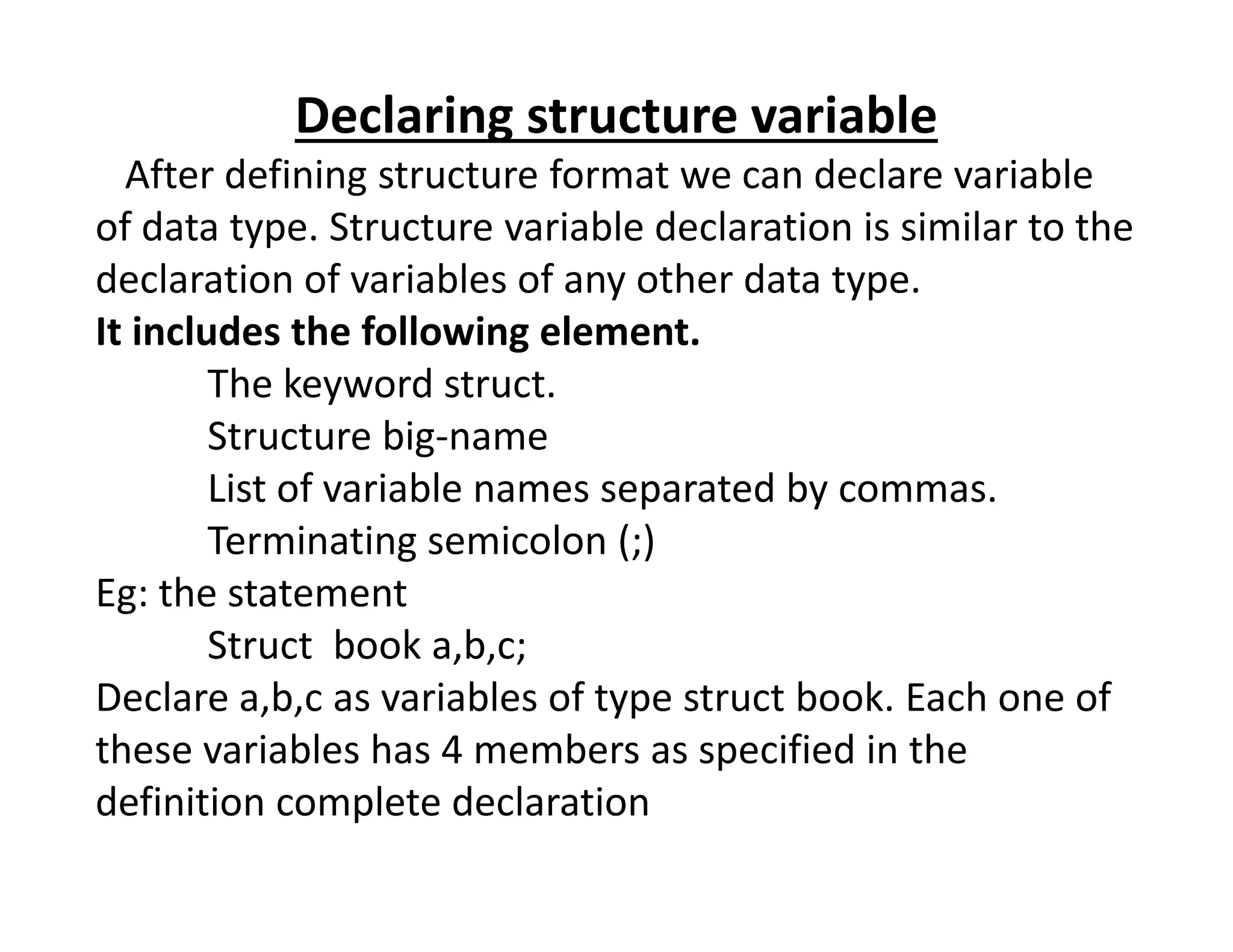
The document discusses structures in C programming. A structure allows grouping of different data types together under one name to represent a record. It defines a structure called "book" with members like title, author, pages, and price to represent a book database. Structure variables can then be declared of this type to store book records. Members of a structure variable can be accessed using the dot operator and assigned values individually.


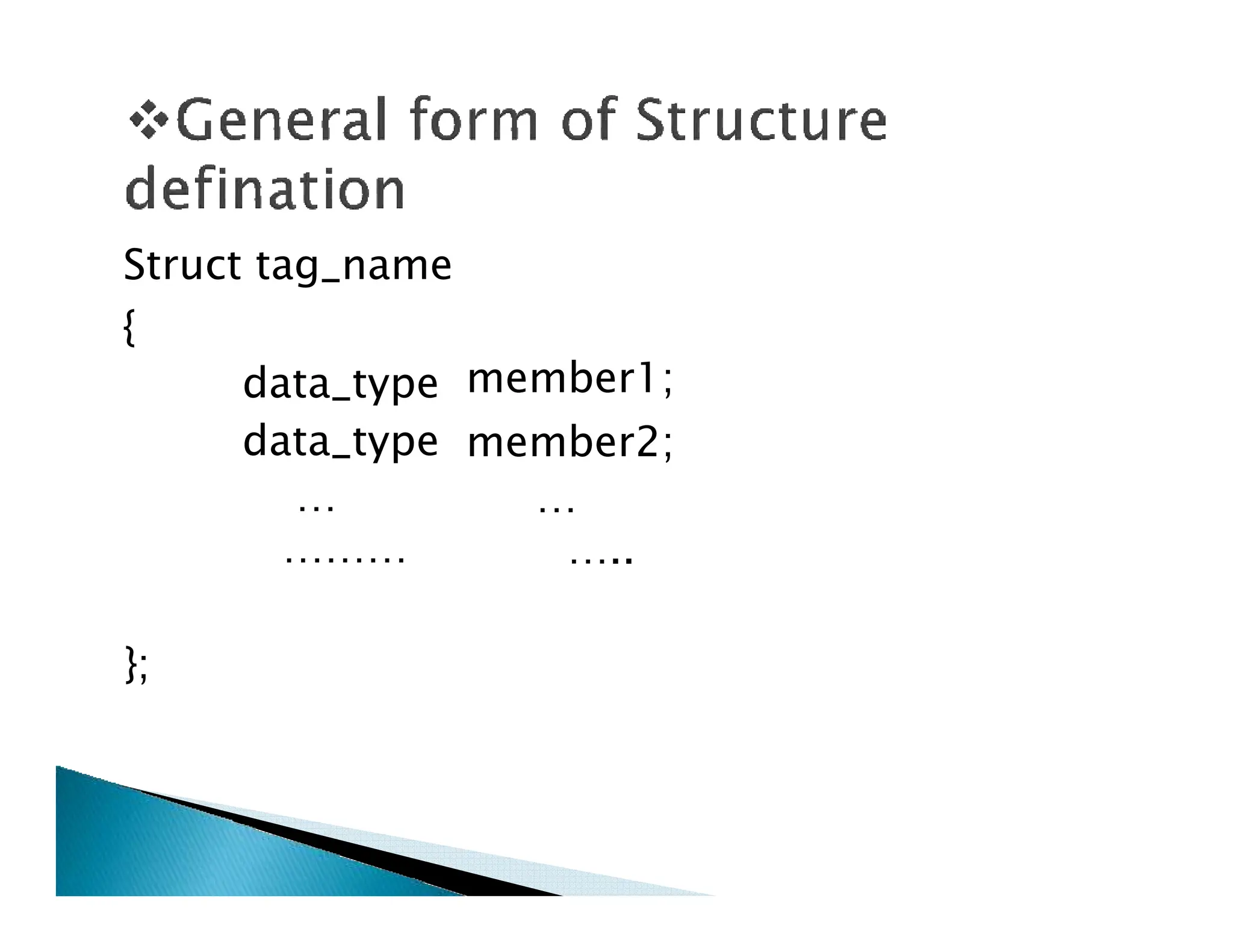

![Struct book
{
Char title[20];
Char author[15];
Int pages;
Int pages;
Float price;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandunion1-231005082134-a928b7f7/75/structure-and-union1-pdf-6-2048.jpg)