The document discusses the use of arrays and structures in C programming, explaining how to declare and use them effectively. It provides examples of one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays, as well as the structure definition and member access syntax. The document also includes an example program that demonstrates user input and output using structures.


![An array is a fixed-size sequenced collection of elements of same data type. ie., it
is a grouping of like-type. So in array a list of items can be given in one variable
name.
The general form of array declaration is
type variable_name[size]
Examples:
int dynami[50];
int trig[50];
int c[50];
float lab[40];
Array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structuresinc-240303095440-2950a739/85/Definition-Declaration-of-Structures-in-C-pptx-3-320.jpg)
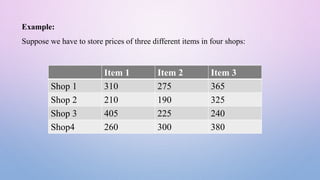
![C allows as to define such tables of item in single variable using two-
dimensional arrays such as
p[4][3]
Two-dimensional array are declared as follows:
Type array_name[row_size][column_size]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structuresinc-240303095440-2950a739/85/Definition-Declaration-of-Structures-in-C-pptx-5-320.jpg)

![struct book_bank
{
char title[20];
char author[15];
int page;
Float price;
};
Definition of Structures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structuresinc-240303095440-2950a739/85/Definition-Declaration-of-Structures-in-C-pptx-7-320.jpg)



![Declaring Structure Variables
The complete variable definition and declaration is
struct book_bank
{
char title[20];
char author[15];
int page;
Float price;
};
struct book_bank, book1, book2, book3;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structuresinc-240303095440-2950a739/85/Definition-Declaration-of-Structures-in-C-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![Declaring Structure Variables
It is also allowed to combine both variable definition and variable
declaration in one step as:
struct book_bank
{
char title[20];
char author[15];
int page;
float price;
} book1, book2, book3;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structuresinc-240303095440-2950a739/85/Definition-Declaration-of-Structures-in-C-pptx-12-320.jpg)



![Example Program
struct personal
{
char name[20];
int day;
char month[10];
float salary;
};
main()
{
structure personal person;
printf(“Input Valuesn”);
scanf(“%s %d %s %f”, person.name,&person.day, &person.month,&person.salary);
printf(“Output Valuesn”);
printf (“%s %d %s %f”, person.name,person.day, person.month,person.salary);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structuresinc-240303095440-2950a739/85/Definition-Declaration-of-Structures-in-C-pptx-16-320.jpg)

