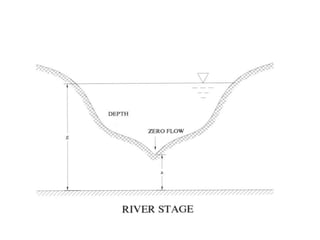
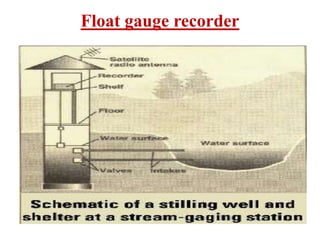
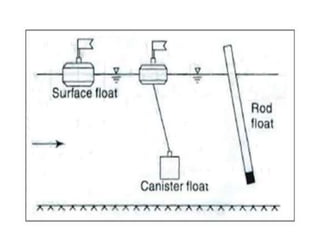
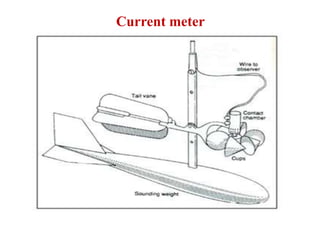
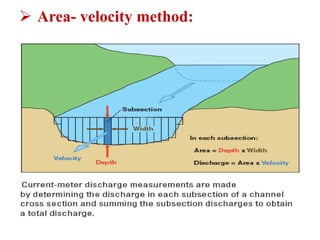
Stream gauging, also known as stream flow measurement, is the measurement of discharge or stream flow passing through a cross section over a period of time. It is important for several reasons, such as forecasting floods, assessing available irrigation water, and determining seasonal runoff variations. When selecting a gauging site, straight reaches with stable cross sections that can measure the full range of high and low flows are preferred. Common stream flow measurement techniques include the area-velocity method, dilution technique, and use of hydraulic structures like weirs and flumes. Stage is also measured, often using staff gauges, to relate water level to discharge measurements.