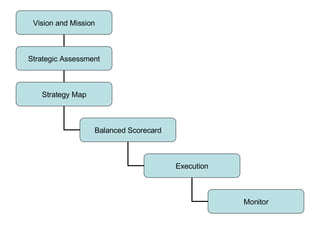
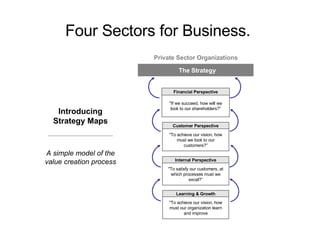
The document discusses creating a balanced scorecard to link organizational objectives, initiatives, and measures to its strategy. It provides an overview of what a balanced scorecard is, noting it measures progress toward strategic goals across financial, customer, internal process, and learning/growth perspectives. It outlines the steps to create a strategy map first to clarify the organization's strategy before developing performance measures in a balanced scorecard.