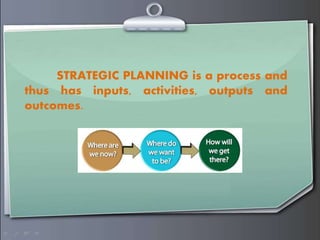
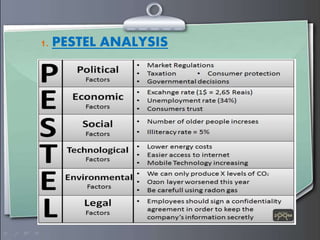
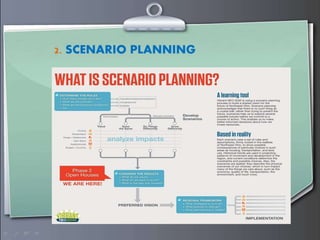
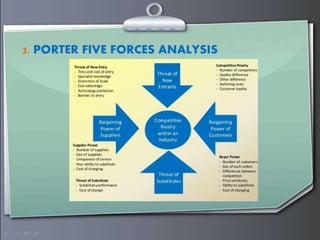
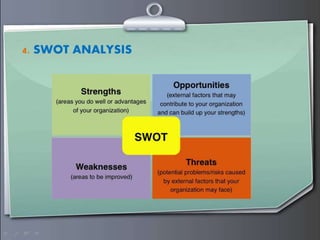
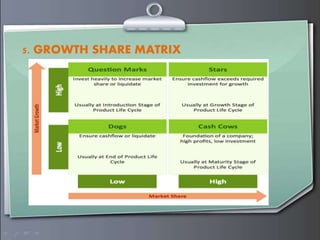
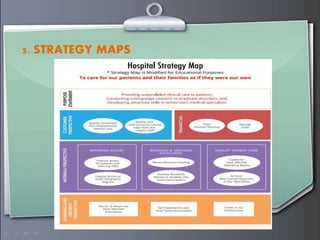
Strategic management involves formulating goals and initiatives by top management based on assessing internal and external environments. Strategic planning defines an organization's strategy and allocates resources to pursue this strategy. It involves gathering input data, strategic planning activities, producing strategic plan outputs, and implementing outcomes. Senior leadership is responsible for determining strategy through a process that can utilize tools like PESTEL analysis, scenario planning, Porter's five forces, SWOT analysis, growth-share matrix, balanced scorecard, and strategy maps.