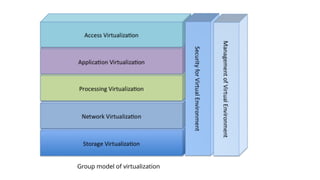
The document discusses virtualization, a technology that allows multiple operating systems and applications to run on a single physical server, utilizing a virtual machine monitor (VMM) for management. It covers various types of virtualization, including hardware, operating system, server, and storage virtualization, along with their advantages and disadvantages. The conclusion emphasizes virtualization's role in enhancing IT resource sharing and cost-efficiency in cloud computing.