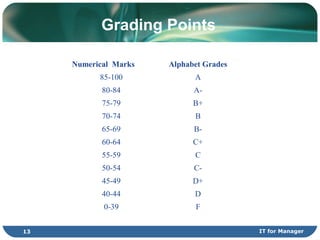
This document provides information on a distributed systems course, including its objectives, learning outcomes, synopsis, content outline, assessment, and grading points. The course aims to provide understanding of distributed systems and emphasize problems, principles, techniques, infrastructure, and applications. Key topics covered include communication, distributed objects, web services, security, naming/trading, time/coordination, concurrency control, transactions, and fault tolerance. Students will be assessed through coursework, a midterm, project, and final exam.