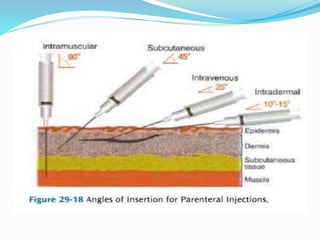
The document discusses parenteral preparations, highlighting their definition, advantages, disadvantages, and various routes of administration. It emphasizes the importance of sterility, stability, and specific requirements for successful formulation and processing of parenteral products, including tests for sterility, clarity, and pyrogen presence. Additionally, it outlines labeling requirements and the necessary production facilities to maintain hygiene during manufacturing.