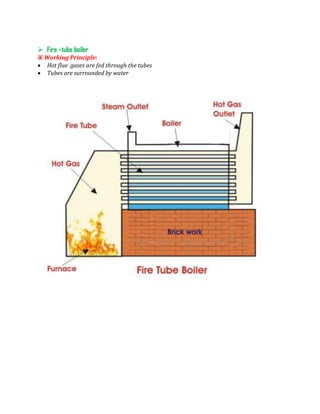
A boiler is a closed vessel that produces steam from water through combustion of fuel. Water is pumped into the boiler and heated by flue gases, vaporizing it into steam. Steam is used for power generation, heating buildings, and industrial processes. There are two main types of boilers - fire-tube boilers where hot gases pass through tubes surrounded by water, and water-tube boilers where water passes through tubes surrounded by hot gases. Water-tube boilers are more efficient but more expensive. Boilers include components like drums, tubes, and mountings to operate safely and control steam production.