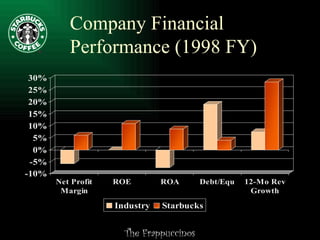
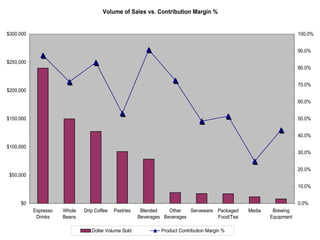
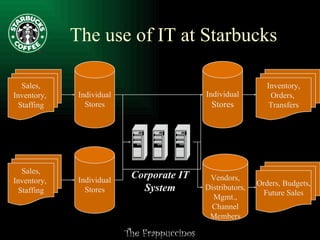
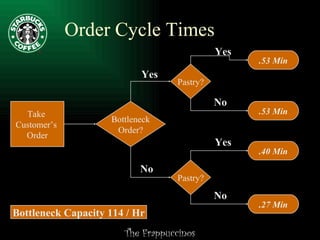
This document summarizes a presentation about improving operations at a specific Starbucks location. It outlines recommendations to: 1) revamp the employee reward system to better motivate workers; 2) tighten the focus on creating a relaxing atmosphere as the "third place"; and 3) measure profitability based on sales of profitable items rather than just reducing labor costs. A three-step action plan is proposed to decrease turnover, improve accessibility and cleanliness, and enhance the store's atmosphere. Potential risks and benefits of the recommendations are also discussed.