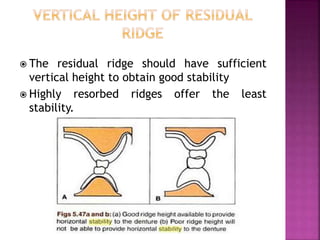
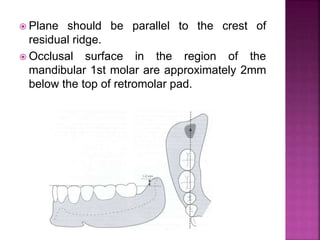
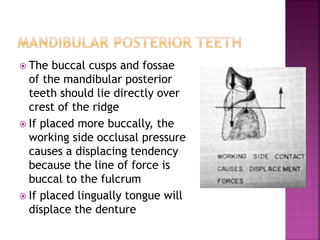
This document discusses the definition and factors affecting the stability of dentures. It defines stability as the ability to resist displacement from functional stresses. The main factors that influence stability are: quality of impression, height of residual ridge, palatal vault shape, arch form, soft tissue quality, lingual flange, occlusal plane, tooth arrangement, polished surface contour, and oral musculature. An accurate impression is important for stability, as is sufficient residual ridge height. Stability is assessed by applying pressure to check for denture tilting.