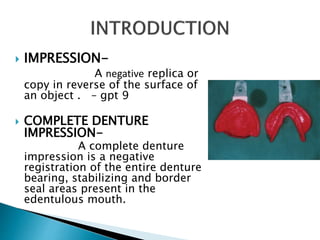
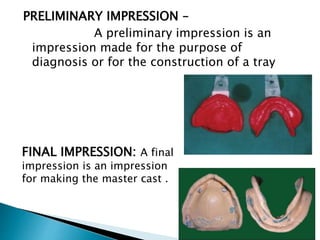
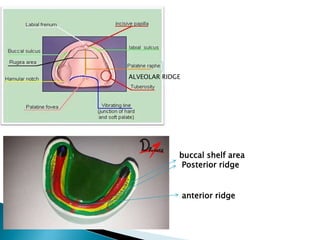
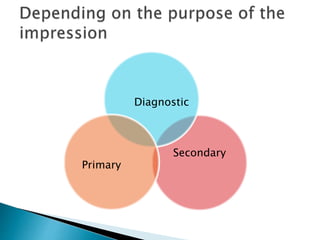
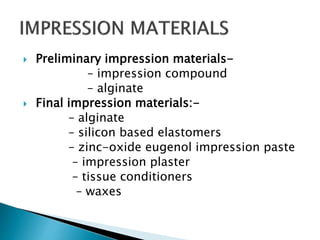
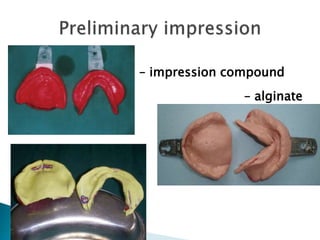
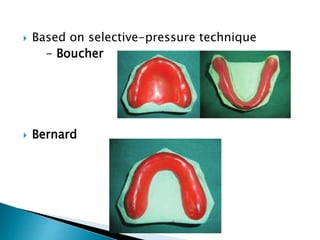
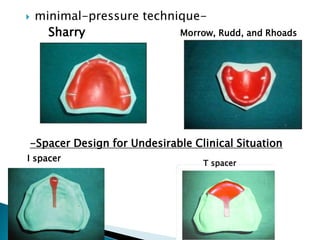
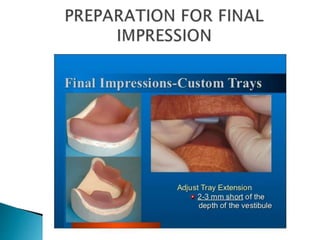
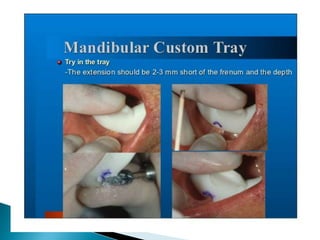
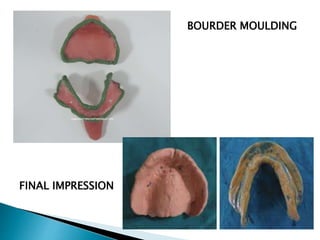
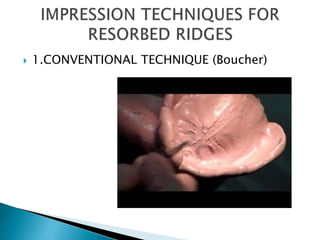
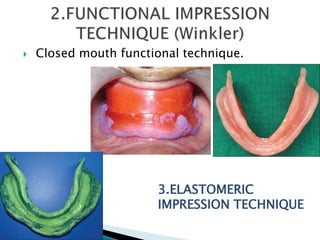
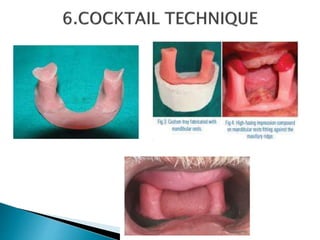
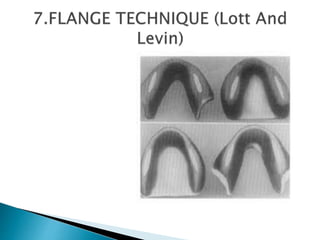
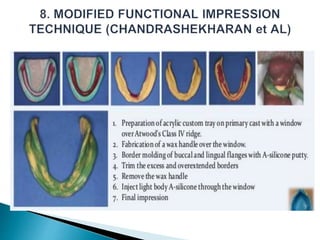
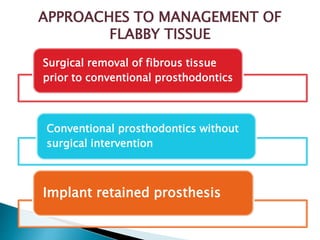
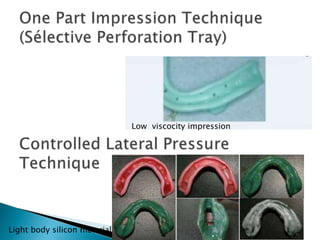
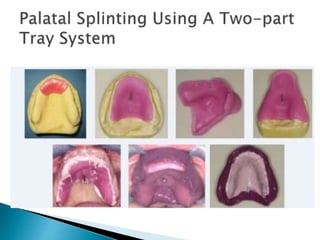
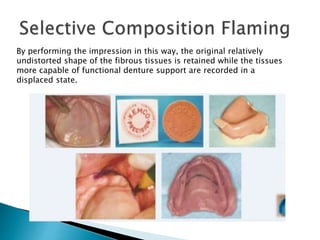
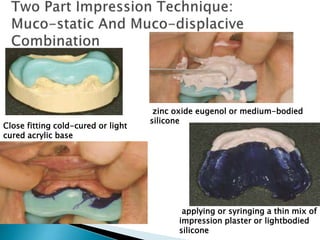
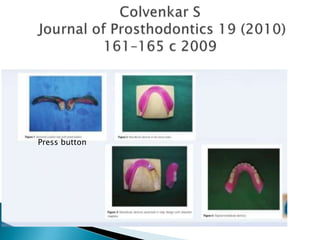
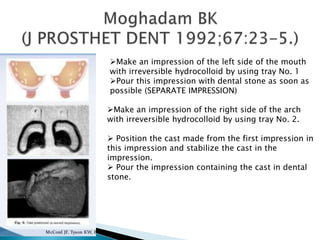
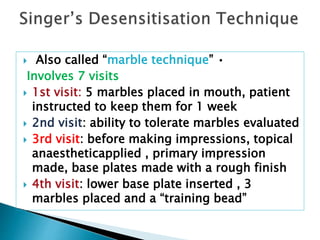
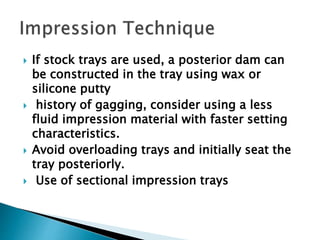
The document covers various aspects of impression making in dentistry, including definitions, techniques, and materials used. It details the differences between preliminary and final impressions, as well as different impression techniques such as mucostatic and mucocompressive. Additionally, it discusses the management of compromised situations and provides insights into patient care and the importance of various impression materials.