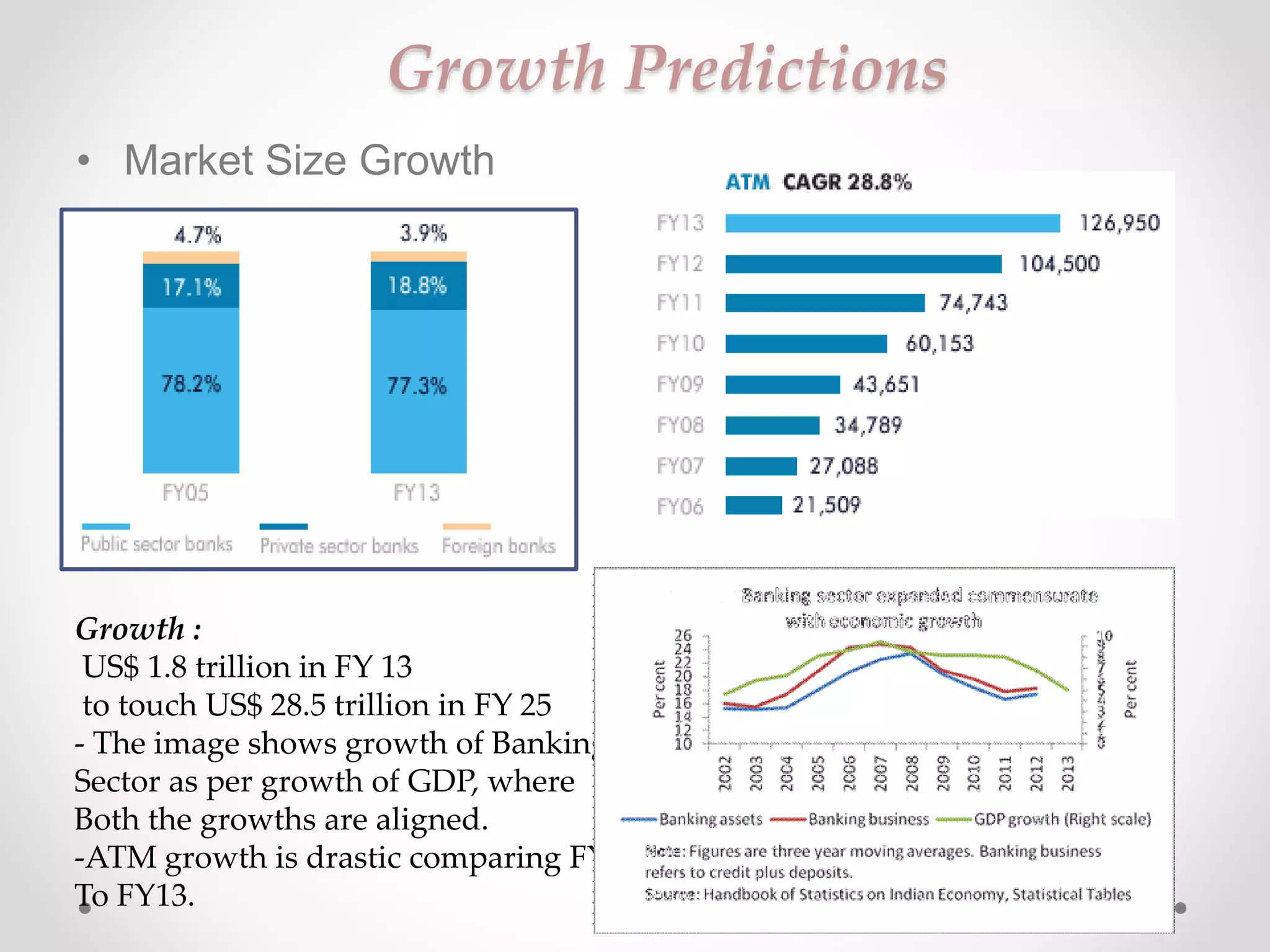
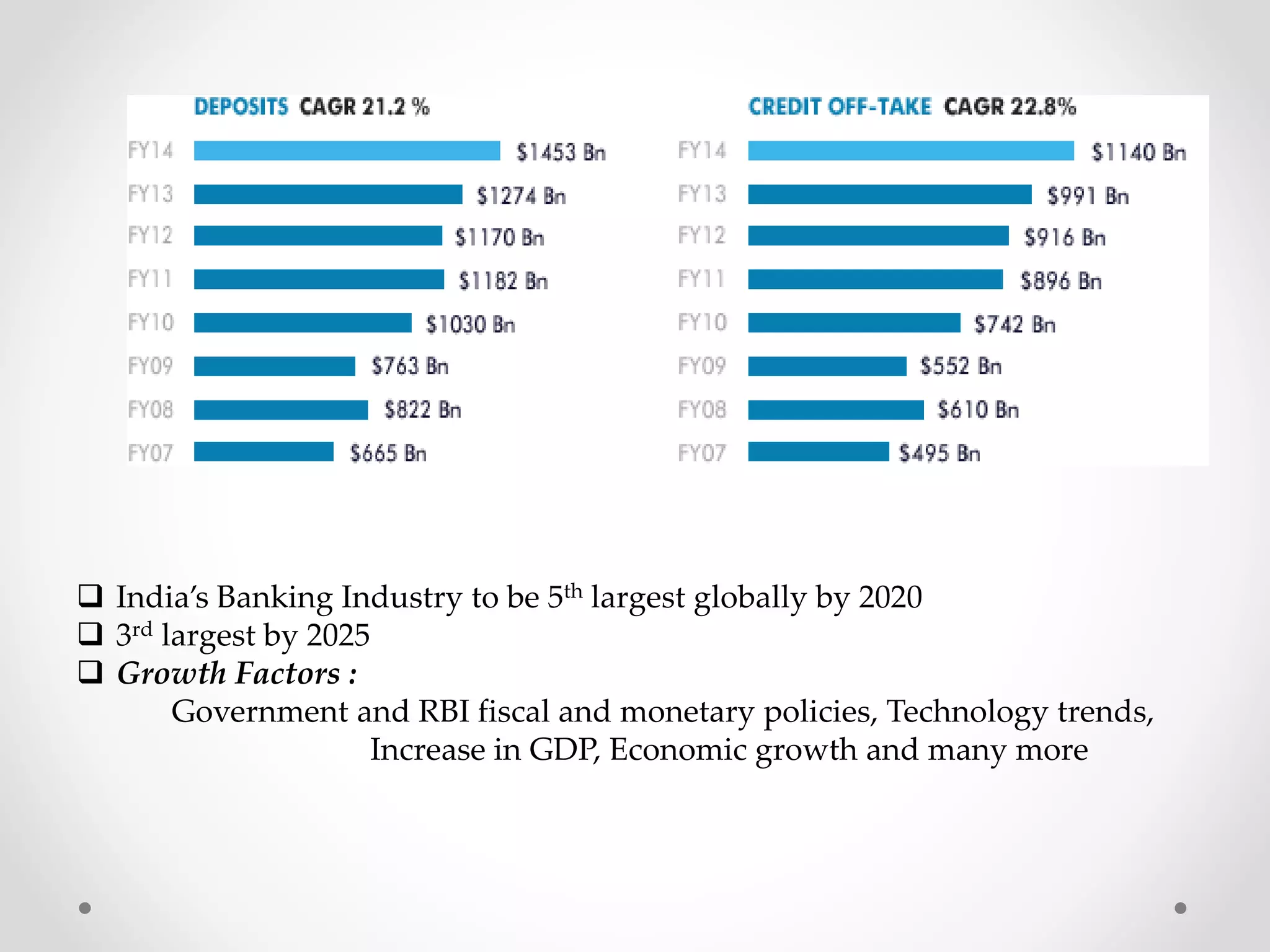
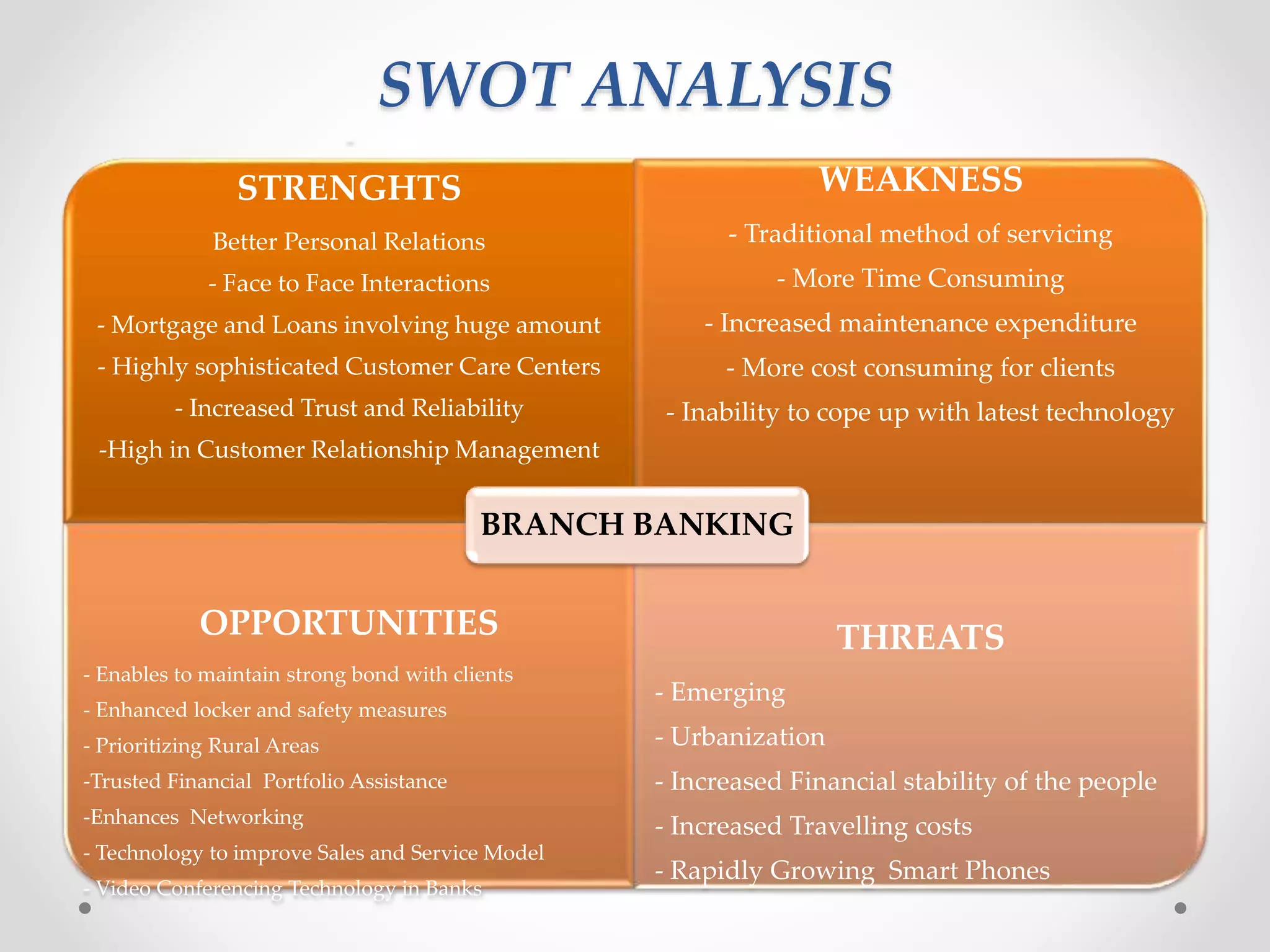
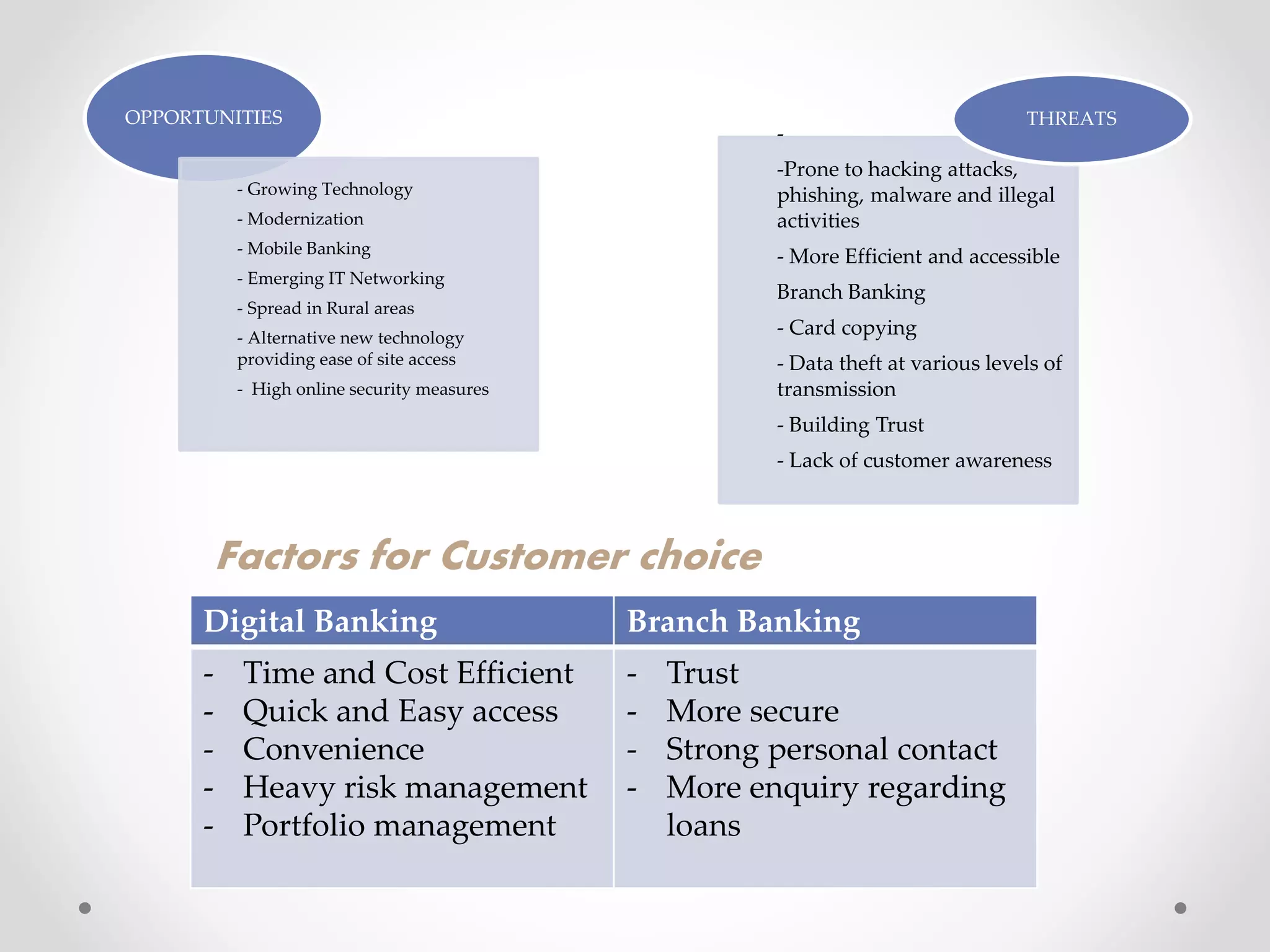
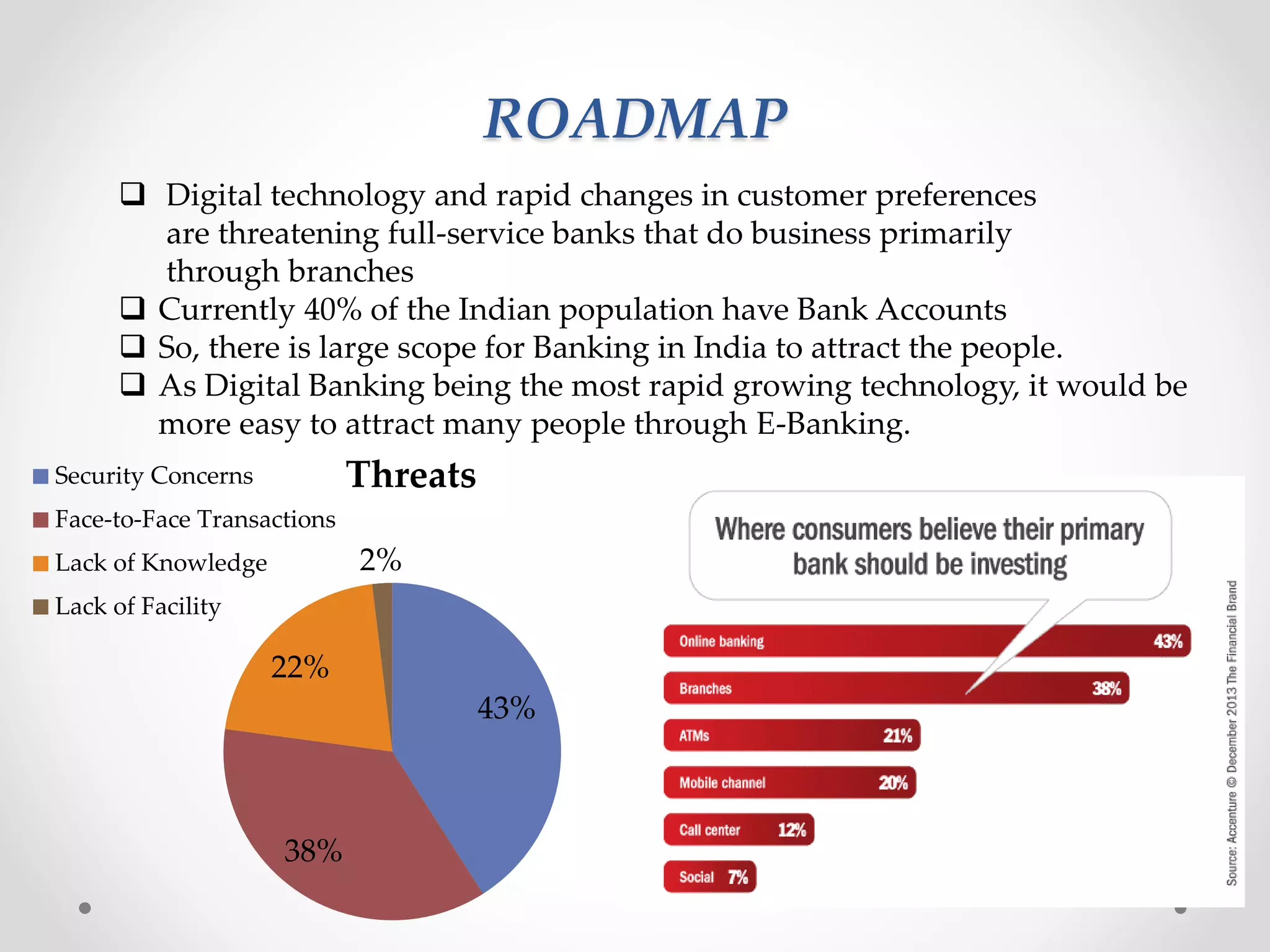
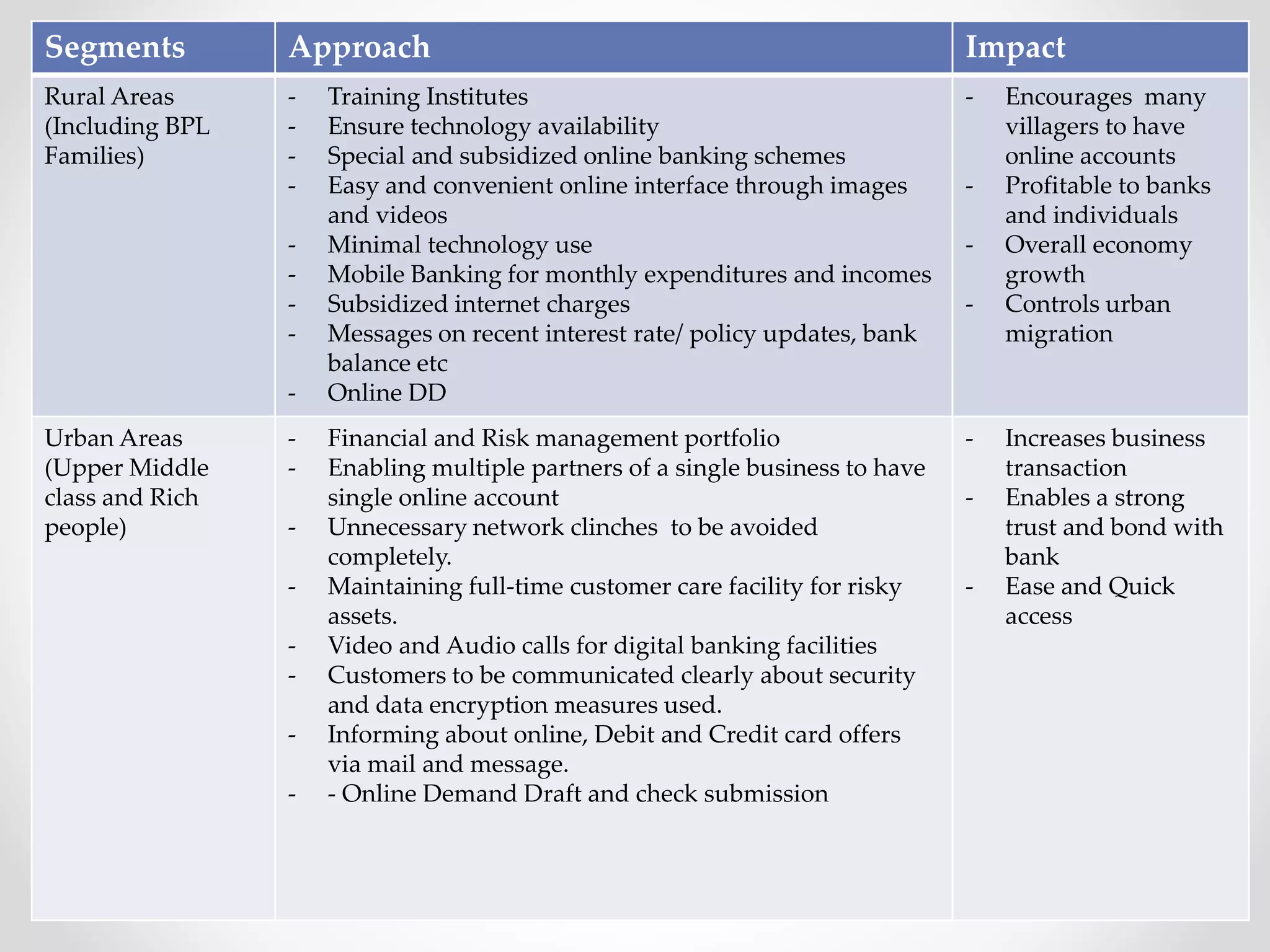
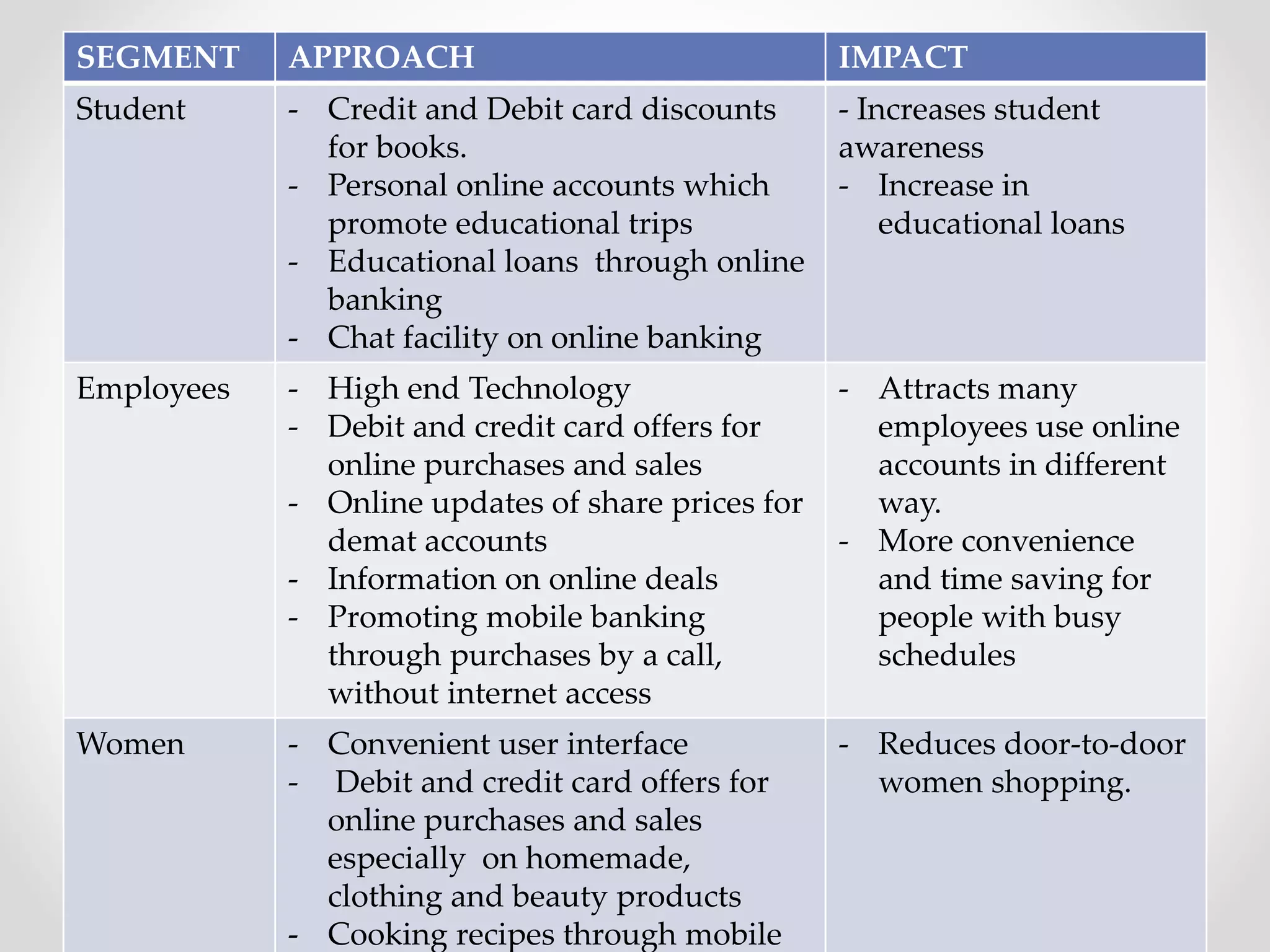
The document analyzes banking in India, comparing branch and digital banking. It finds that while branch banking offers personal connections, digital banking provides convenience and accessibility. A survey showed students prefer digital banking, while older people prefer branches. The document proposes a long-term roadmap to promote digital banking segment-wise, especially in rural areas, to increase inclusion while addressing issues like security, access, and lack of knowledge.