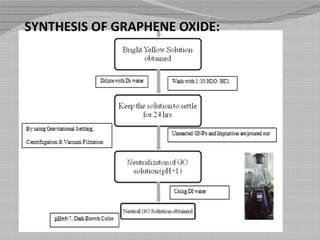
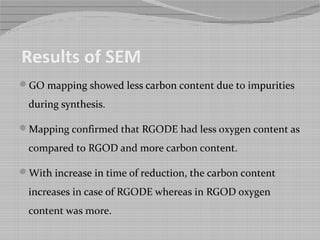
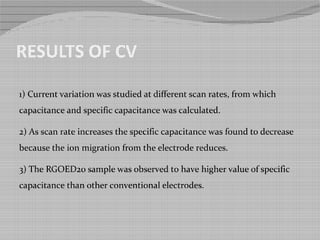
This document outlines a study on producing nitrogen enriched carbon coated graphene scaffolds for use in supercapacitors. Graphene oxide was synthesized using a modified Hummer's method and then reduced to produce reduced graphene oxide. Some samples were further modified by enriching with nitrogen and coating with carbon from glucose. Characterization with SEM, UV spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry showed the nitrogen enriched carbon coated reduced graphene oxide had higher porosity, lower oxygen content and higher specific capacitance, making it a promising electrode material for capacitive energy storage.