The document outlines the virtualization of high-performance servers using Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) with KVM on Debian Jessie, specifically leveraging Intel X520 10Gbps network cards. It covers prerequisites, hardware setup, BIOS configurations, kernel requirements, and the process for implementing SR-IOV to achieve near bare-metal performance for virtual machines. Additionally, it includes steps for creating virtual functions, networking configurations using libvirt, and the necessary commands for managing the setup.



![6/19
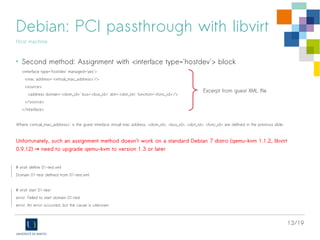
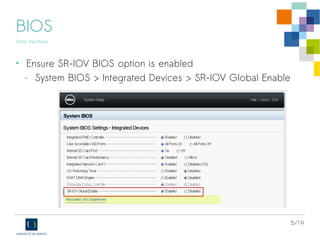
BIOS
Host machine
• Ensure SR-IOV BIOS option is enabled
- Device Settings > [Select NIC] > Device Level Configuration
> Virtualization mode = SR-IOV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sr-iov-intel-debian-140620012427-phpapp01/85/SR-IOV-KVM-and-Intel-X520-10Gbps-cards-on-Debian-Stable-6-320.jpg)
![7/19
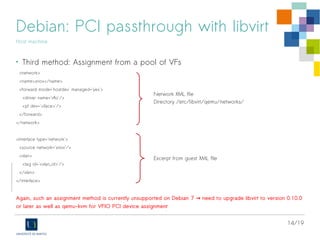
BIOS
Host machine
• Ensure SR-IOV BIOS option is enabled
- Device Settings > [Select NIC] > NIC Configuration
> PCI Virtual Functions Advertised = 64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sr-iov-intel-debian-140620012427-phpapp01/85/SR-IOV-KVM-and-Intel-X520-10Gbps-cards-on-Debian-Stable-7-320.jpg)

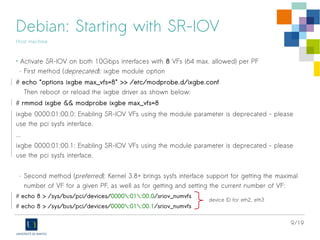
![10/19
Debian: Starting with SR-IOV
Host machine
• Check for SR-IOV hardware support on NICs:
# lspci -v
…
42:00.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation Ethernet 10G 2P X520 Adapter (rev 01)
Subsystem: Intel Corporation 10GbE 2P X520 Adapter
...
Capabilities: [160] Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV)
Kernel driver in use: ixgbe
42:00.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation Ethernet 10G 2P X520 Adapter (rev 01)
Subsystem: Intel Corporation 10GbE 2P X520 Adapter
...
Capabilities: [160] Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV)
Kernel driver in use: ixgbe
eth0
eth1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sr-iov-intel-debian-140620012427-phpapp01/85/SR-IOV-KVM-and-Intel-X520-10Gbps-cards-on-Debian-Stable-10-320.jpg)
![11/19
Debian: Starting with SR-IOV
Host machine
• Check for Intel's VT-d IOMMU support:
# dmesg | egrep -i “DMA|IOMMU”
…
Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-3.16.0-4-amd64 root=UUID=821747a0-fe42-473c-9273-391feb7f82cf
ro intel_iommu=on quiet
Intel-IOMMU: enabled
...
dmar: IOMMU 0: reg_base_addr d5000000 ver 1:0 cap d2078c106f0466 ecap f020de
dmar: IOMMU 1: reg_base_addr df900000 ver 1:0 cap d2078c106f0466 ecap f020de
...
IOMMU: Setting identity map for device 0000:00:1f.0 [0x0 - 0xffffff]
PCI-DMA: Intel(R) Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O
…
https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/vfio.txt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sr-iov-intel-debian-140620012427-phpapp01/85/SR-IOV-KVM-and-Intel-X520-10Gbps-cards-on-Debian-Stable-11-320.jpg)