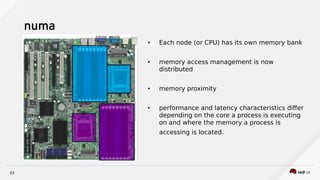
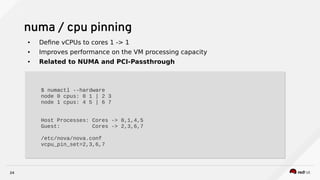
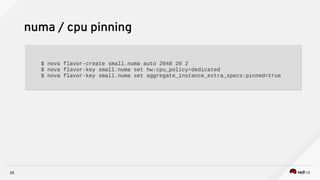
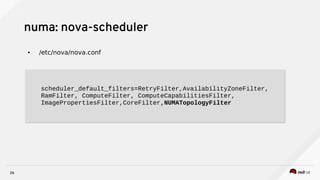
Raul Leite discusses several key NFV concepts and bottlenecks including:
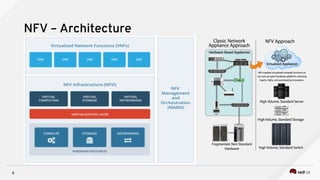
1) NFV architecture which aims for independent hardware, automatic network operation, and flexible application development.
2) Common NFV bottlenecks like packet loss, hypervisor overhead, and low throughput due to CPU and resource allocation issues.
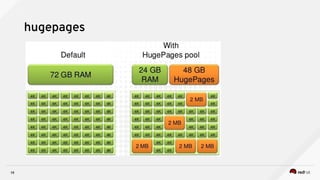
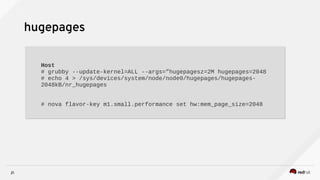
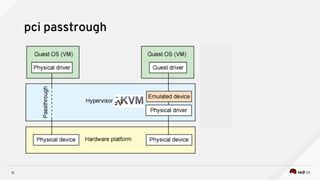
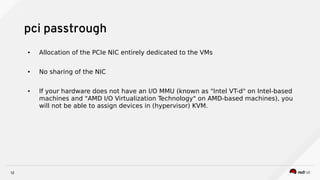
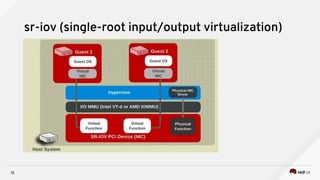
3) Techniques to optimize NFV performance such as SR-IOV, PCI passthrough, hugepages, CPU pinning, and DPDK. SR-IOV and PCI passthrough provide direct access to network hardware while hugepages, pinning and DPDK improve CPU performance.








![17
sr-iov
# lspci -nn | grep -i 82576
05:00.0 Ethernet controller [0200]: Intel Corporation 82576 Gigabit
Network Connection [8086:10c9] (rev 01)
05:10.0 Ethernet controller [0200]: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual
Function [8086:10ca] (rev 01)
# neutron net-create nfv_sriov --shared --provider:network_type vlan
--provider:physical_network physnet_sriov
--provider:segmentation_id=2150
# neutron subnet-create --name nfv_subnet_sriov --disable-dhcp
--allocation-pool start=10.0.5.2,end=10.0.5.100 nfv_sriov 10.0.5.0/24
# neutron port-create nfv_sriov --name sriov-port --binding:vnic-type
direct
# lspci -nn | grep -i 82576
05:00.0 Ethernet controller [0200]: Intel Corporation 82576 Gigabit
Network Connection [8086:10c9] (rev 01)
05:10.0 Ethernet controller [0200]: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual
Function [8086:10ca] (rev 01)
# neutron net-create nfv_sriov --shared --provider:network_type vlan
--provider:physical_network physnet_sriov
--provider:segmentation_id=2150
# neutron subnet-create --name nfv_subnet_sriov --disable-dhcp
--allocation-pool start=10.0.5.2,end=10.0.5.100 nfv_sriov 10.0.5.0/24
# neutron port-create nfv_sriov --name sriov-port --binding:vnic-type
direct](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knownbasicofnfvfeaturesv2-161027113712/85/Known-basic-of-NFV-Features-17-320.jpg)