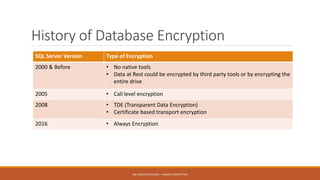
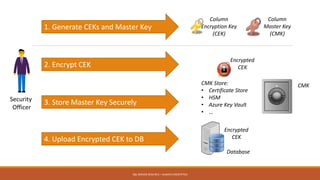
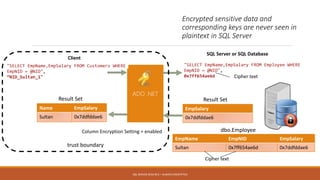
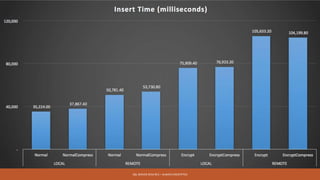
Md. Sultan-E-Alam Khan gave a presentation on SQL Server 2016 RC3's new Always Encrypted feature for database encryption. Always Encrypted allows encryption of sensitive data in client applications so encryption keys are never revealed to SQL Server. It works by having client applications encrypt data with column encryption keys before inserting into SQL Server tables, where the encrypted data and encrypted column encryption keys are stored. This provides encryption of data in use, in motion and at rest without requiring changes to the database schema or application code. The presentation covered the history of database encryption, how Always Encrypted works, key types, encryption methods, limitations and a demo.