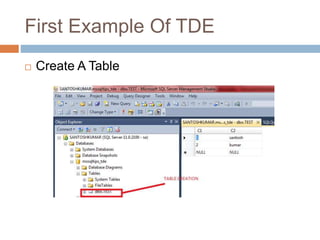
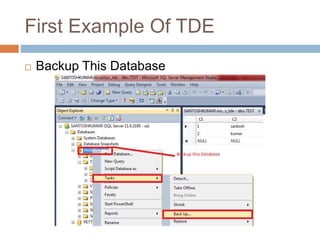
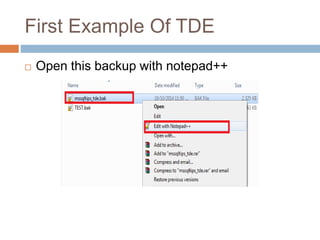
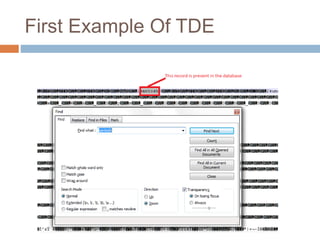
The document discusses various database concepts including indexing, hashing, and encryption. It provides details on:
- The different types of indexes (clustered, non-clustered, unique) and when to use each.
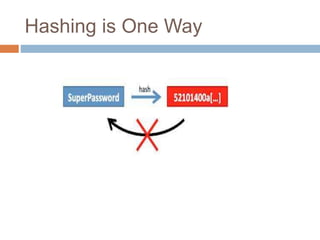
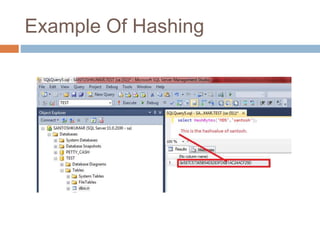
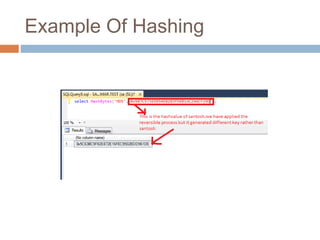
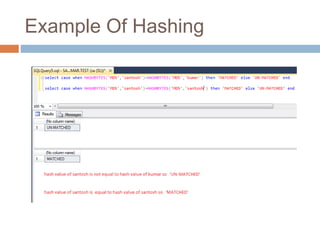
- Hashing algorithms like MD5 and SHA that are used to securely store passwords.
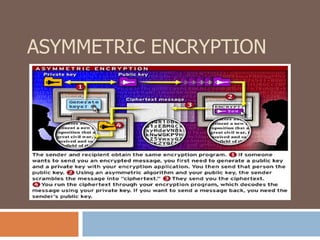
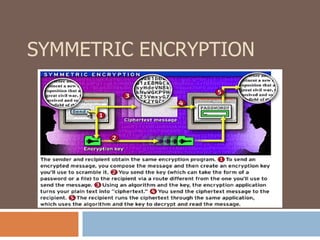
- The differences between asymmetric and symmetric encryption, with asymmetric being more secure but slower.
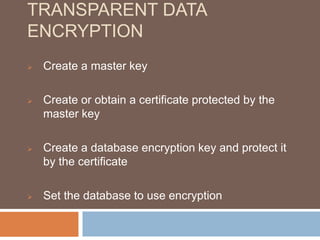
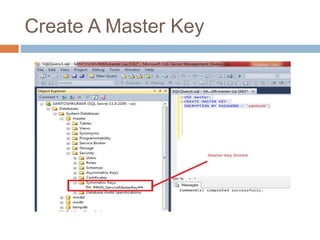
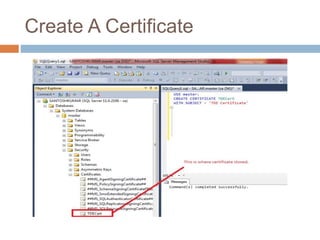
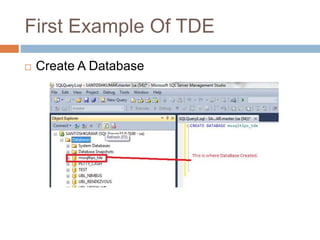
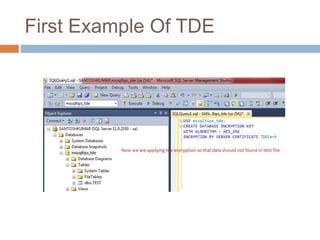
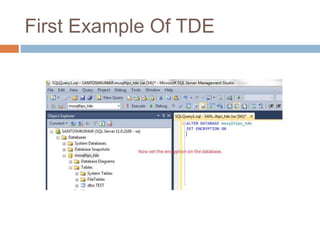
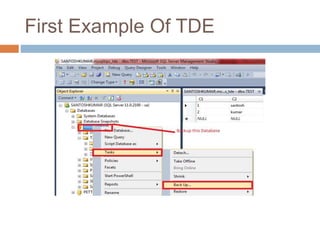
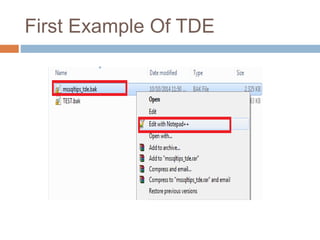
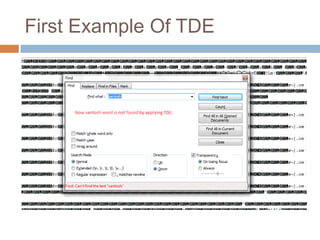
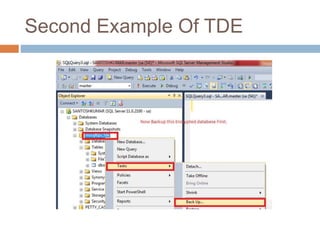
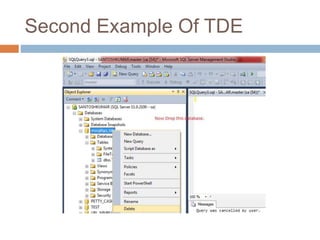
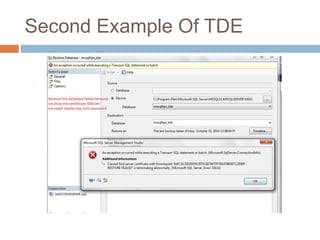
- Transparent data encryption in SQL Server 2008 that performs real-time encryption of data files transparently without requiring code changes.