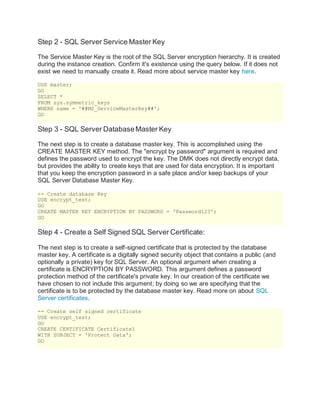
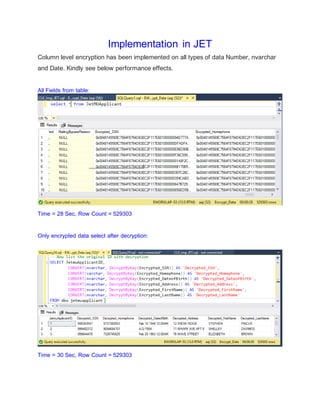
This document outlines the steps to encrypt columns in a SQL Server table containing sensitive data using symmetric key encryption. The steps include: 1) creating a database master key to provide encryption capabilities; 2) creating a self-signed certificate and symmetric key protected by the database master key; 3) altering the table to add an encrypted column and encrypting the sensitive data; and 4) decrypting the data by opening the symmetric key. Encrypting columns helps protect sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, if unauthorized access is gained to the database.