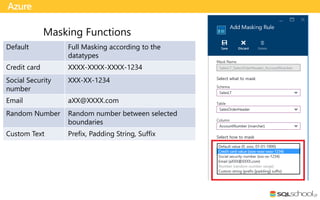
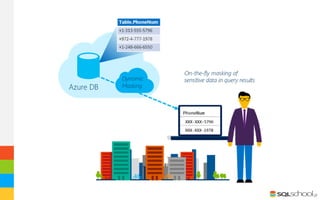
Dynamic data masking is a data protection feature in SQL Server 2016 that masks sensitive data in query results without altering the actual data. It can help protect private information by exposing only obfuscated data to unauthorized users. Administrators can configure masking rules for specific columns using various masking functions like default, email, random, or custom string masking. The underlying data remains intact but masked data is returned for users without unmask permissions. It provides data security with minimal performance impact by masking results on-the-fly.














![Random
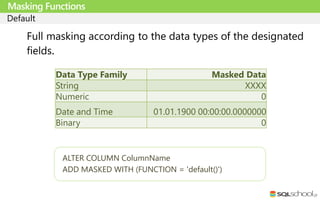
Masking Functions
ALTER COLUMN ColumnName
ADD MASKED WITH (FUNCTION = 'random([start range], [end range])')
A random masking function for use on any numeric type to
mask the original value with a random value within a
specified range.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicdatamaskingsqlserver2016-160612112736/85/Dynamic-data-masking-sql-server-2016-18-320.jpg)
![Custom String (Partial)
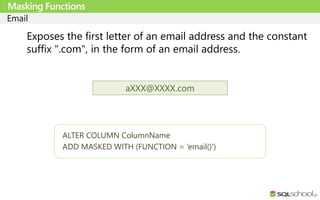
Masking Functions
ALTER COLUMN ColumnName
ADD MASKED WITH (FUNCTION = ‘partial(prefix,[padding],suffix)’
Exposes the first and last letters and adds a custom padding
string in the middle
• Phone: partial(4,”XXXXXXXXXXX”,0)
• Credit Card: partial(0,”XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-”,4)
• Email: partial(1,”xxxx@xxxx.”,2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicdatamaskingsqlserver2016-160612112736/85/Dynamic-data-masking-sql-server-2016-19-320.jpg)