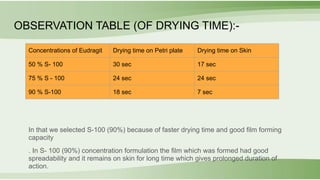
The document outlines the formulation and evaluation of a synthetic spray bandage using camphor and eugenol, highlighting key ingredients, methods, and evaluation parameters. It details the selection of polymers and their properties, particularly comparing Eudragit S-100 and RS-100, and examines drying times, spreadability, and diffusion of the drug. The results indicate that Eudragit S-100 at 90% concentration provides optimal film-forming capacity and patient compliance, leading to the conclusion that this formulation is effective for topical drug delivery.