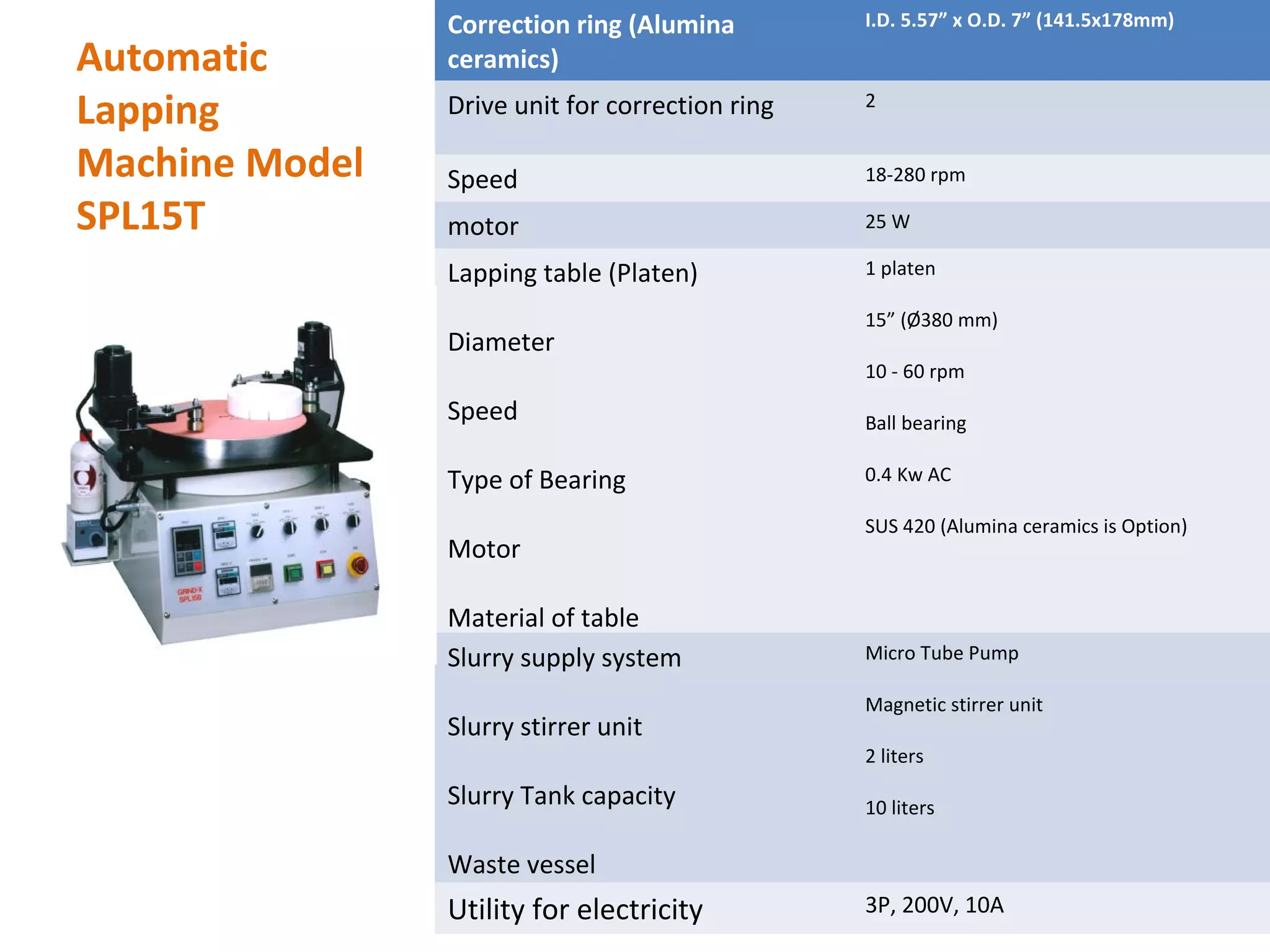
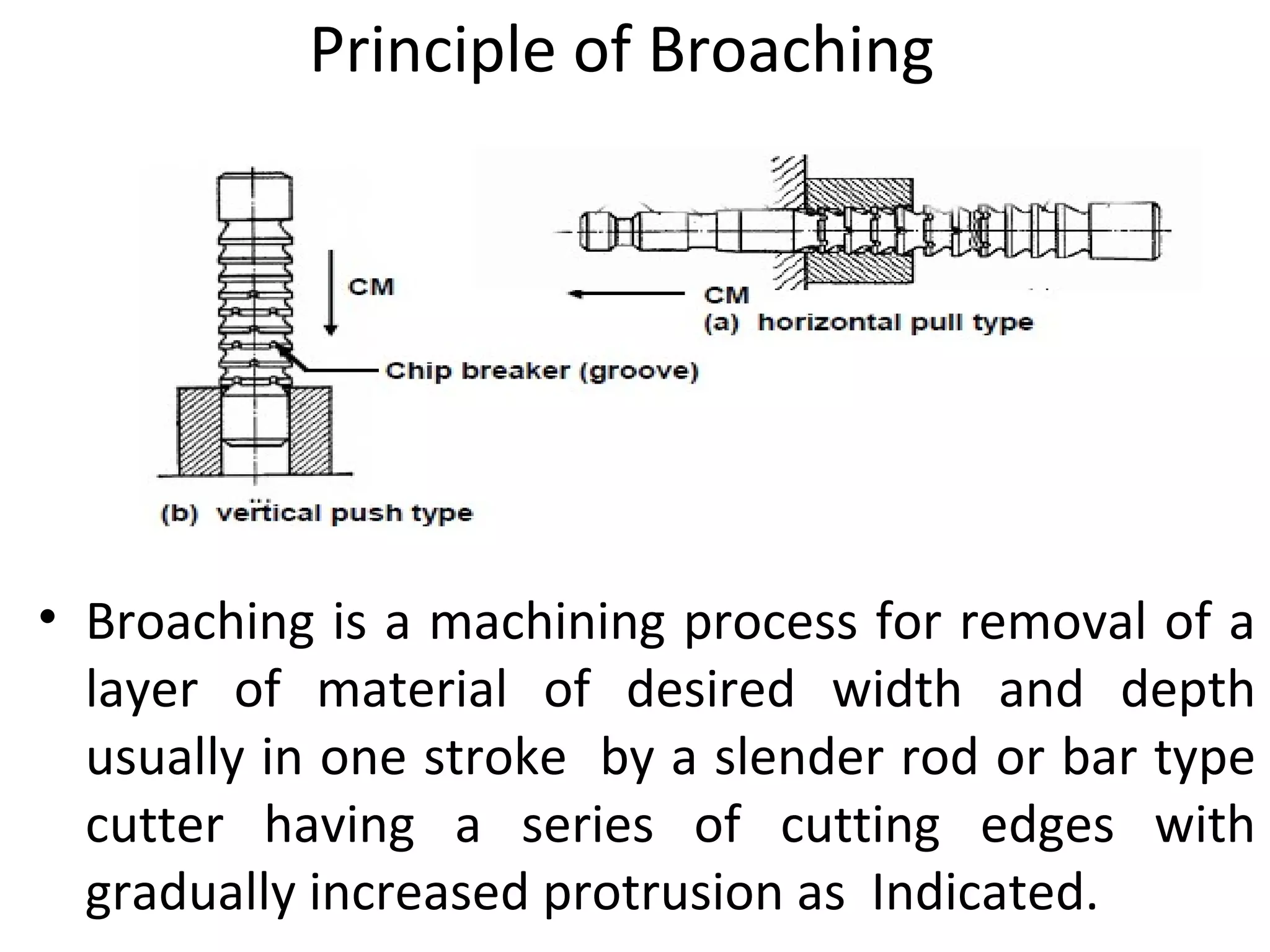
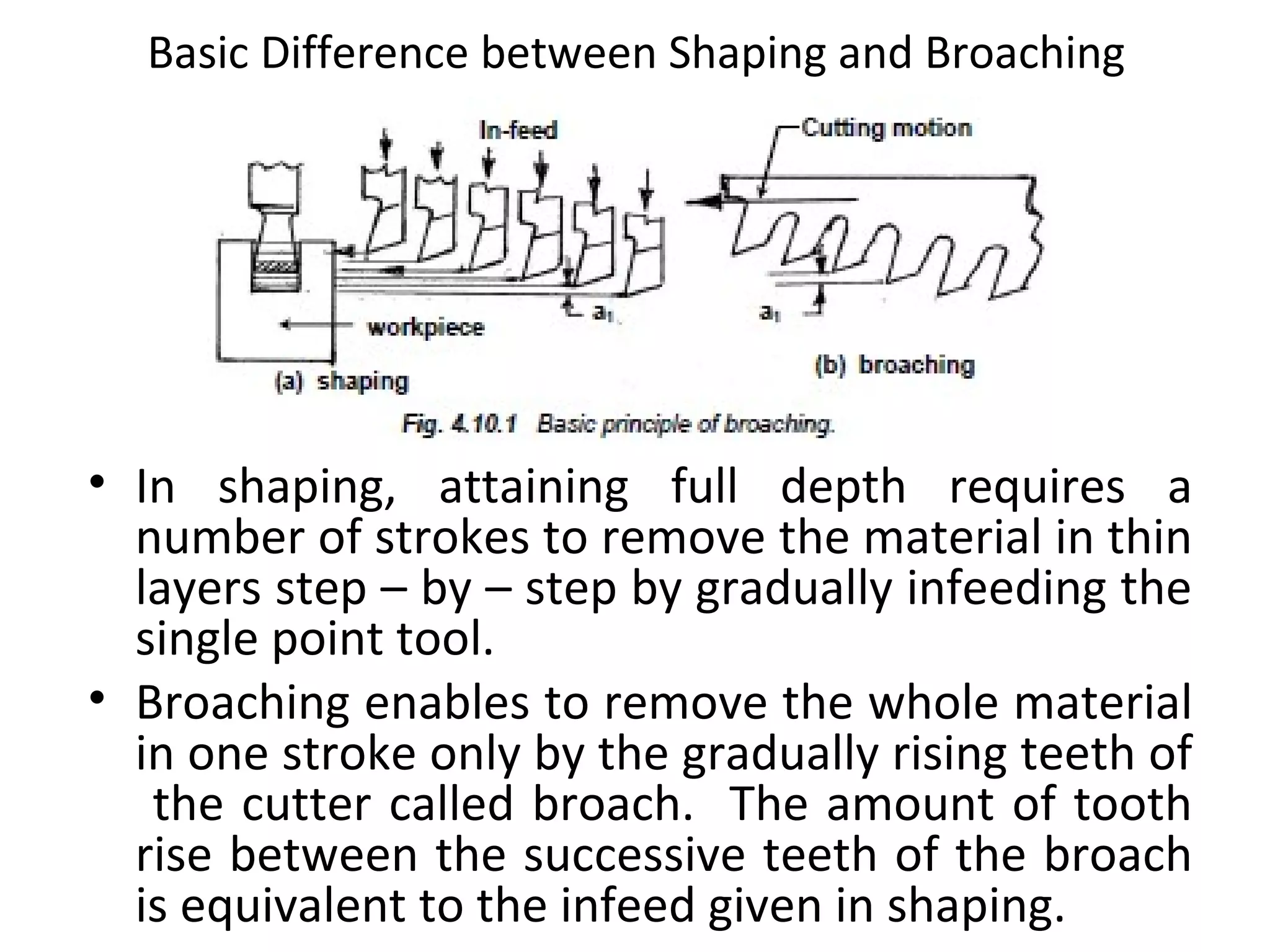
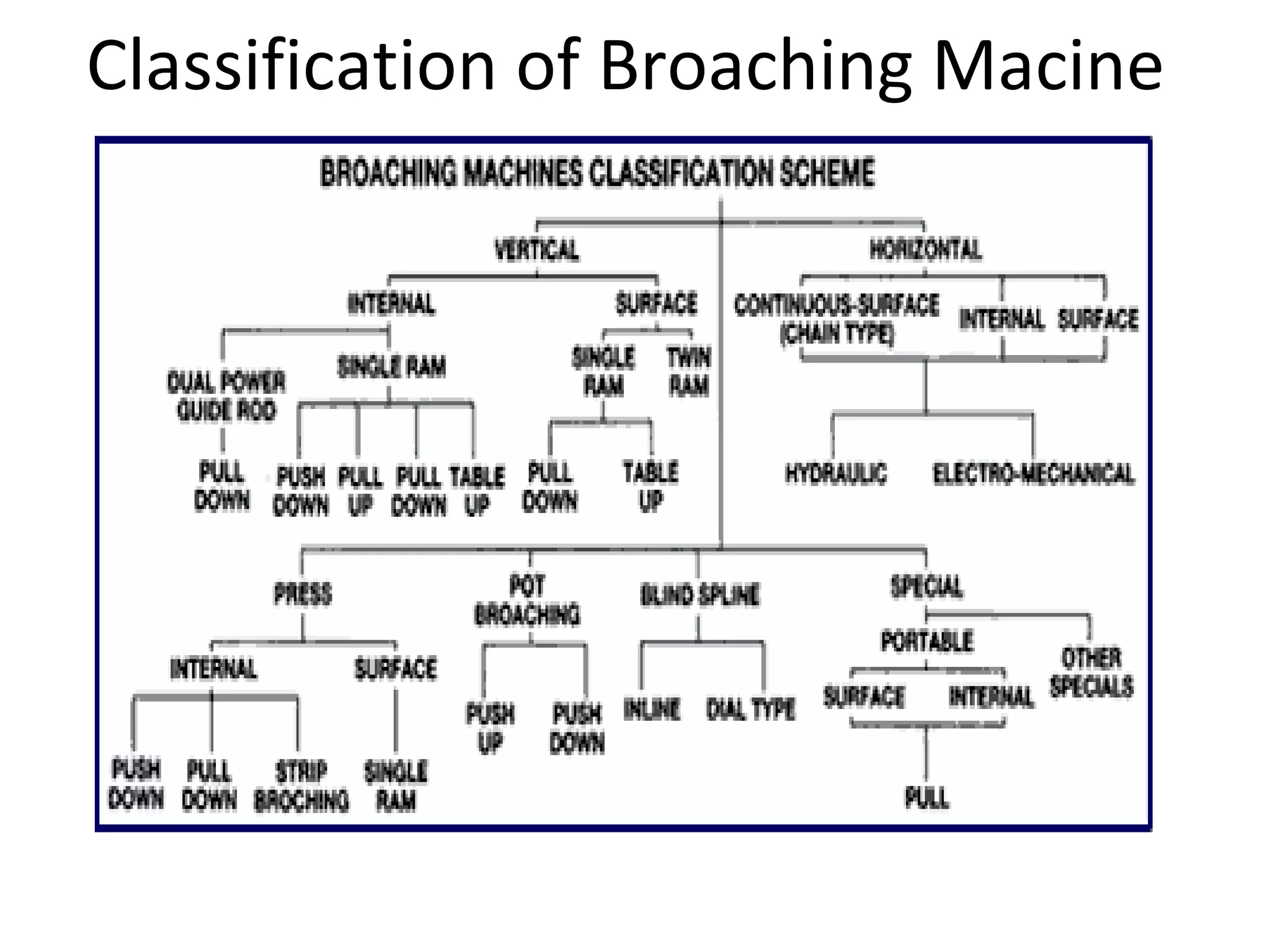
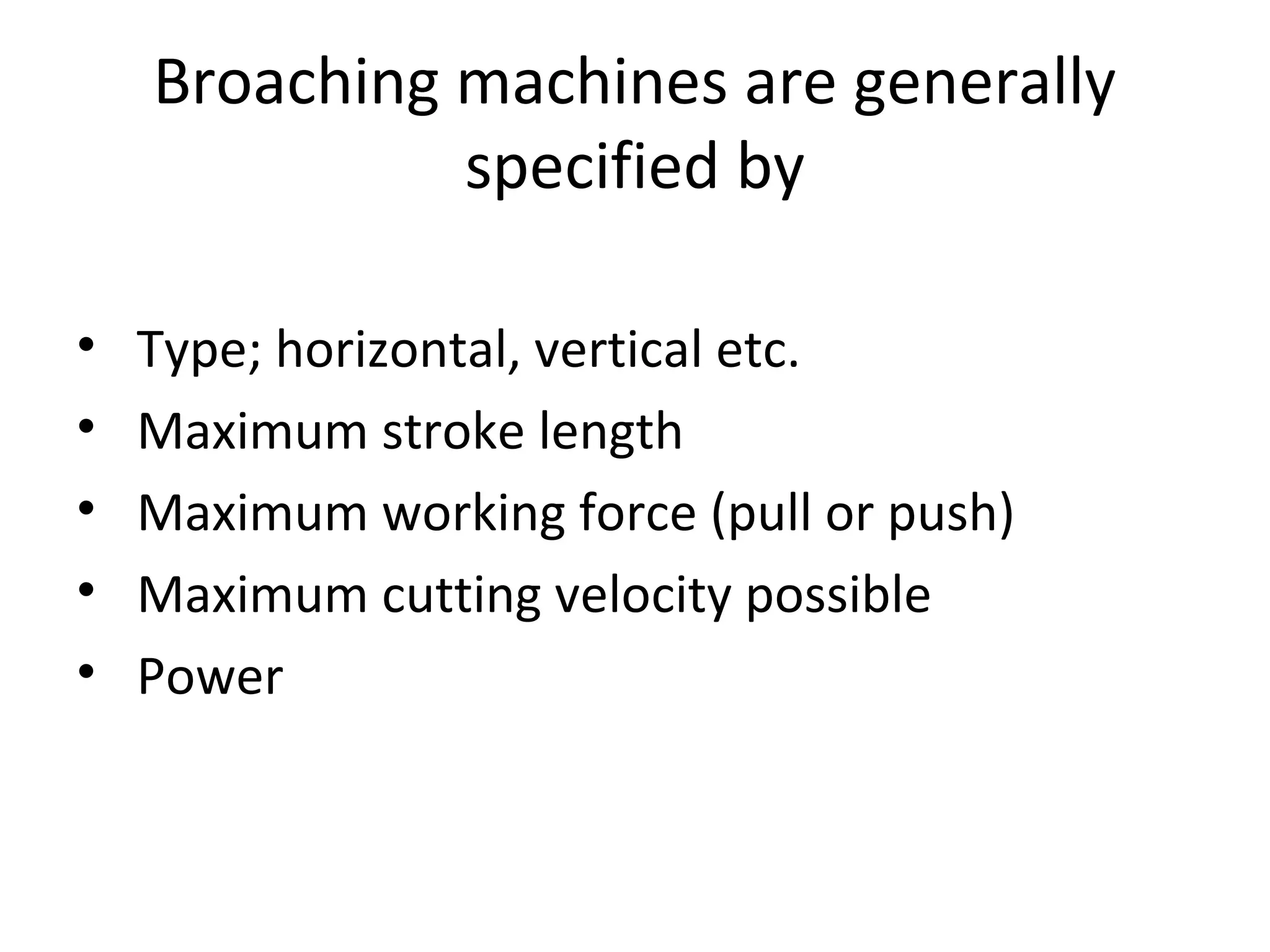
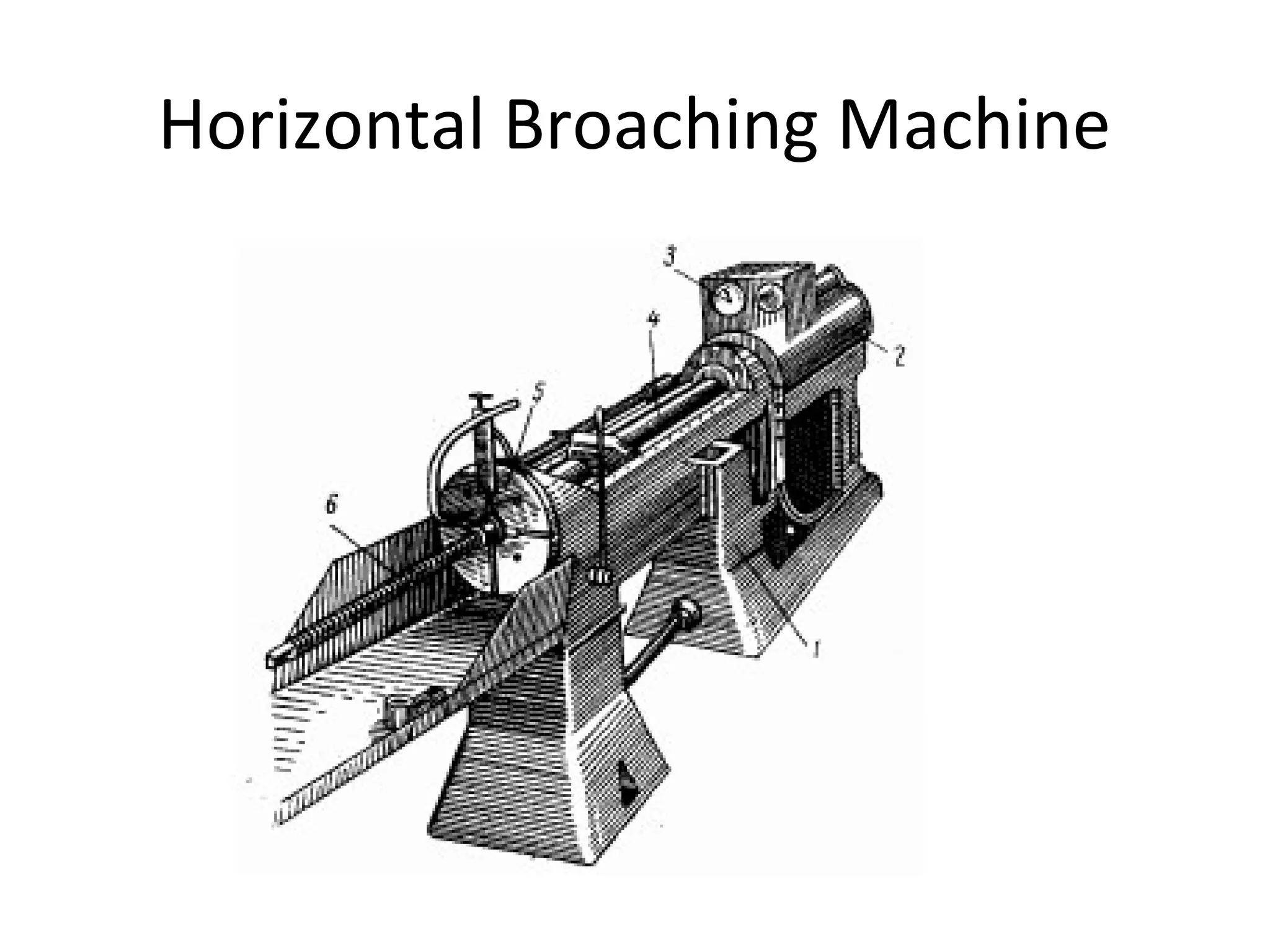
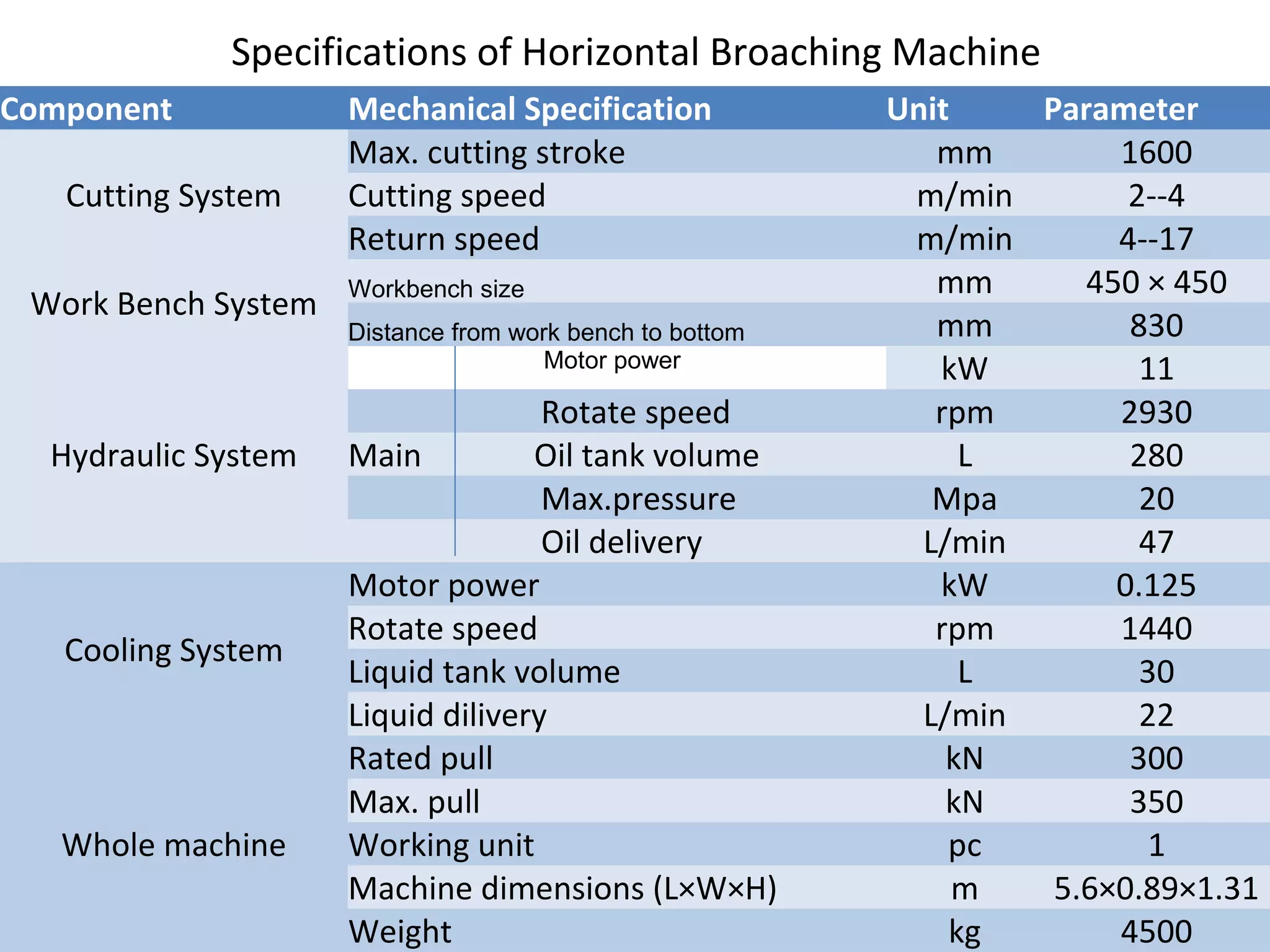
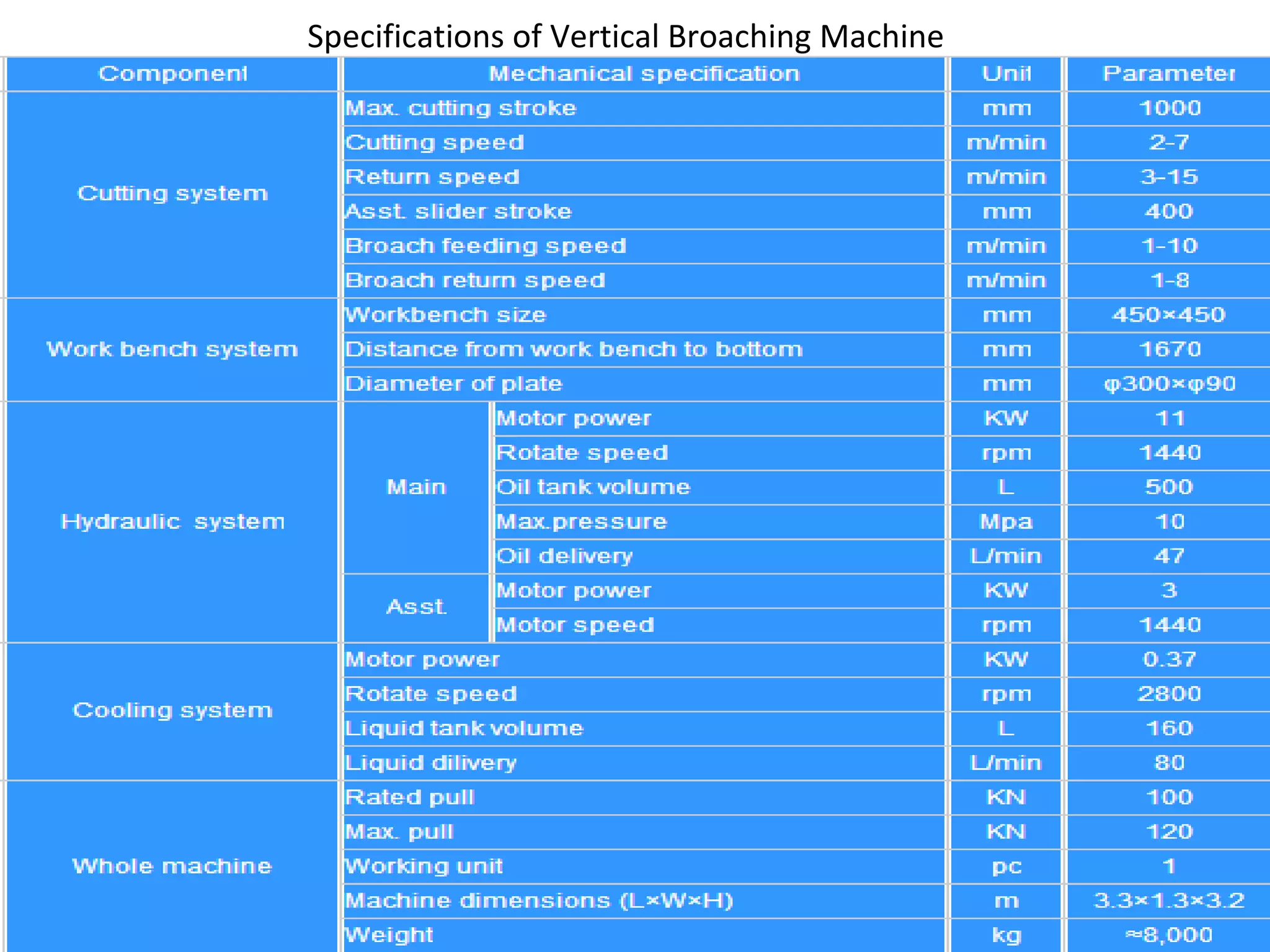
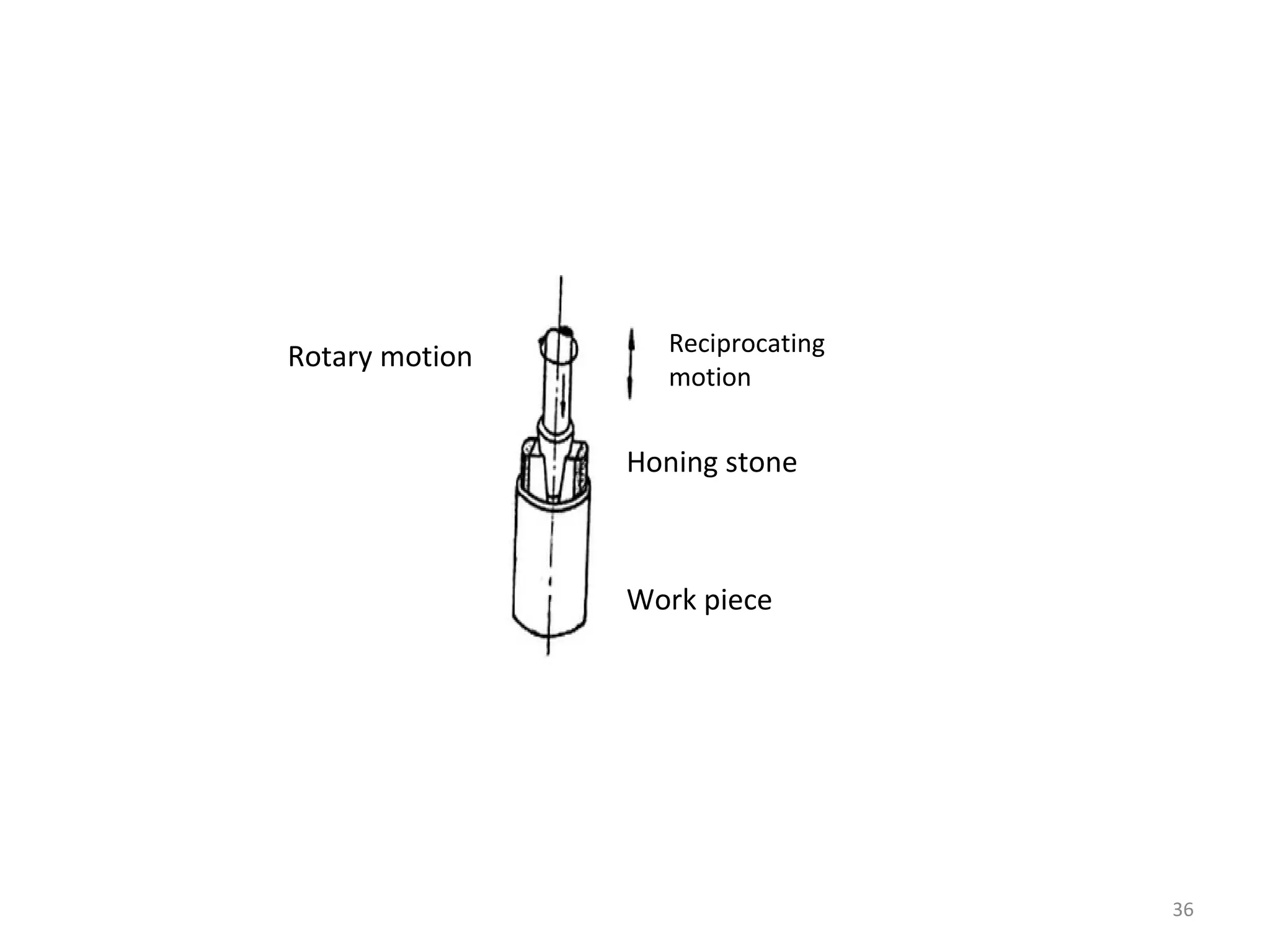
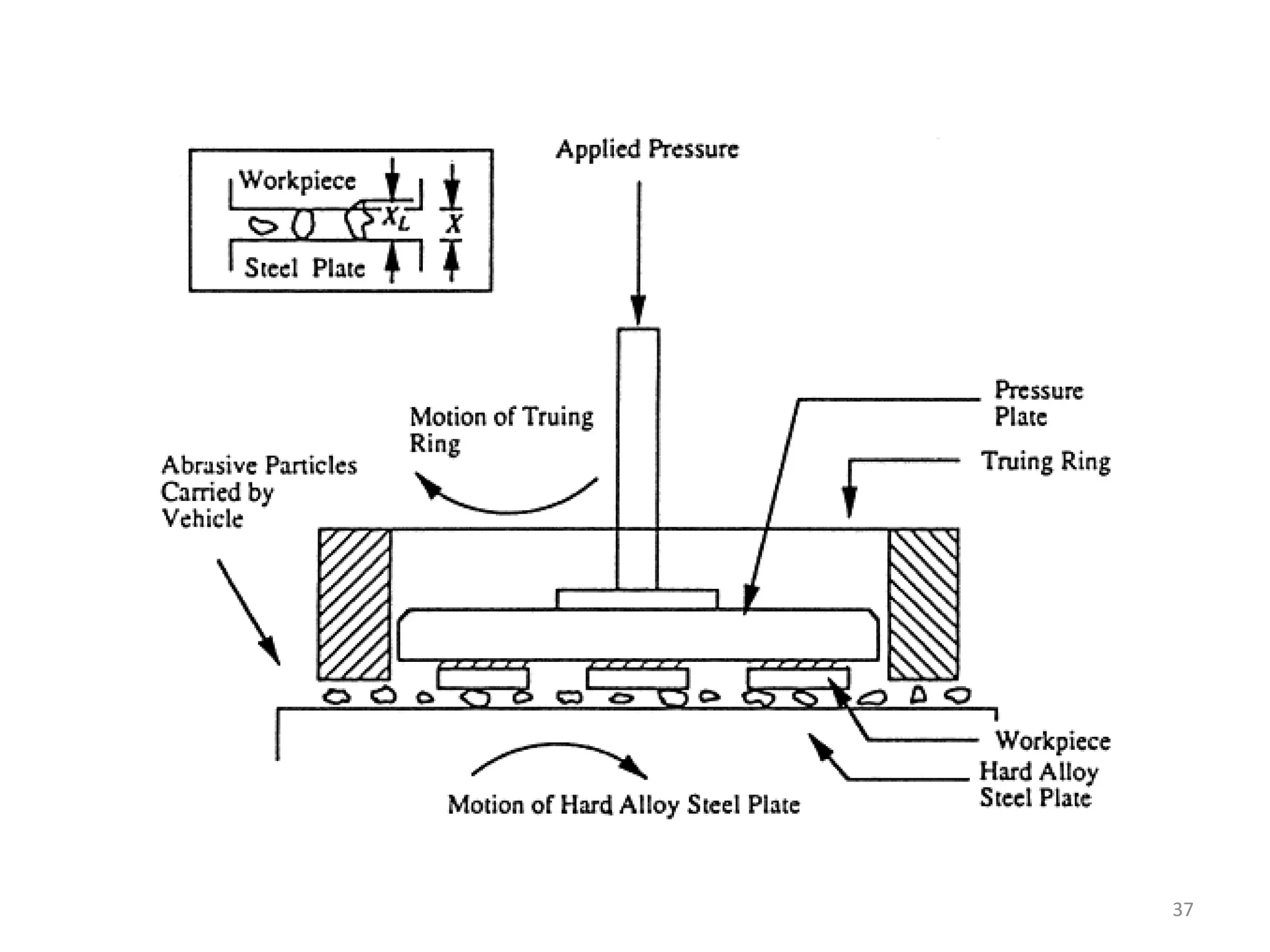
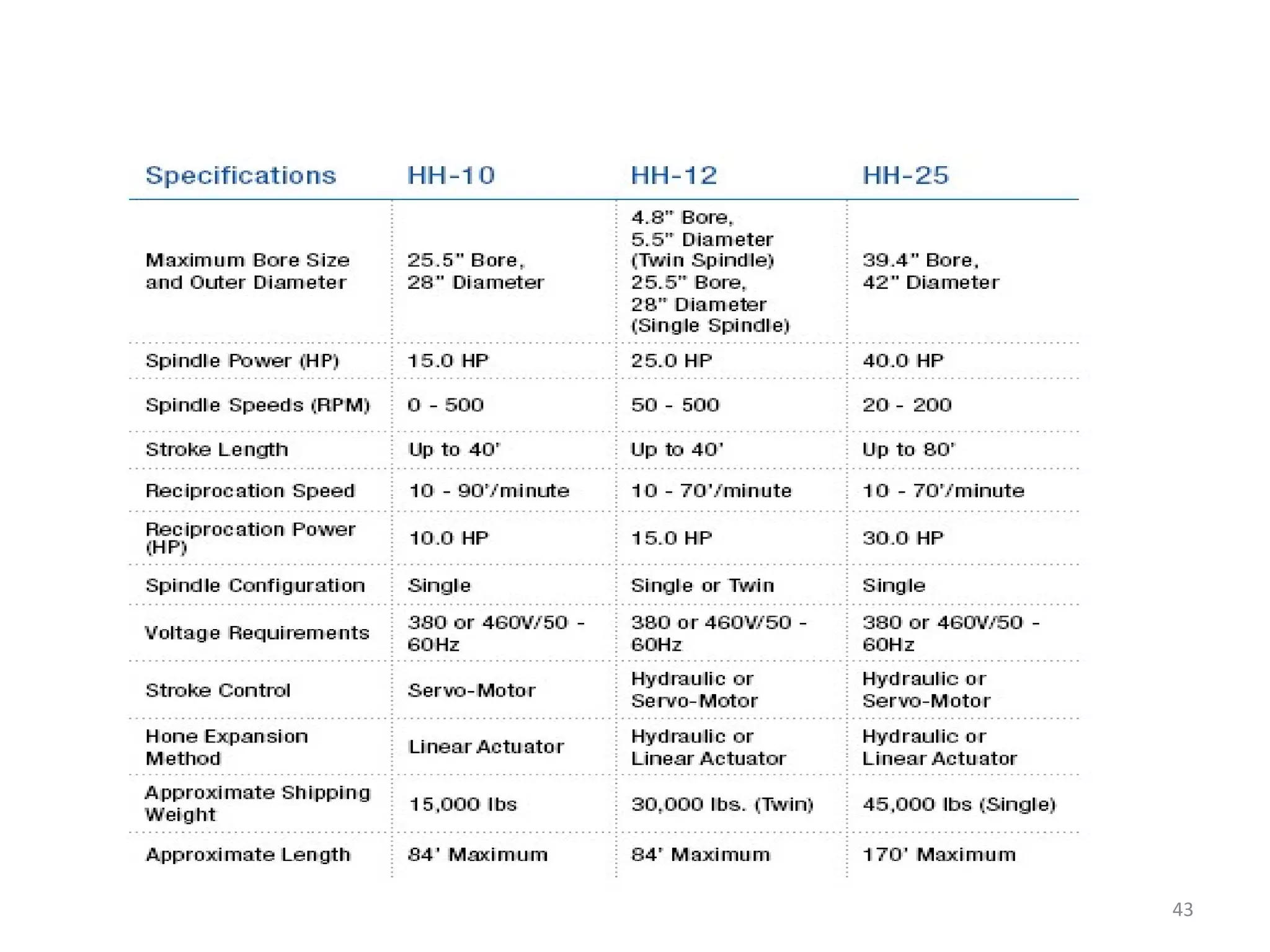
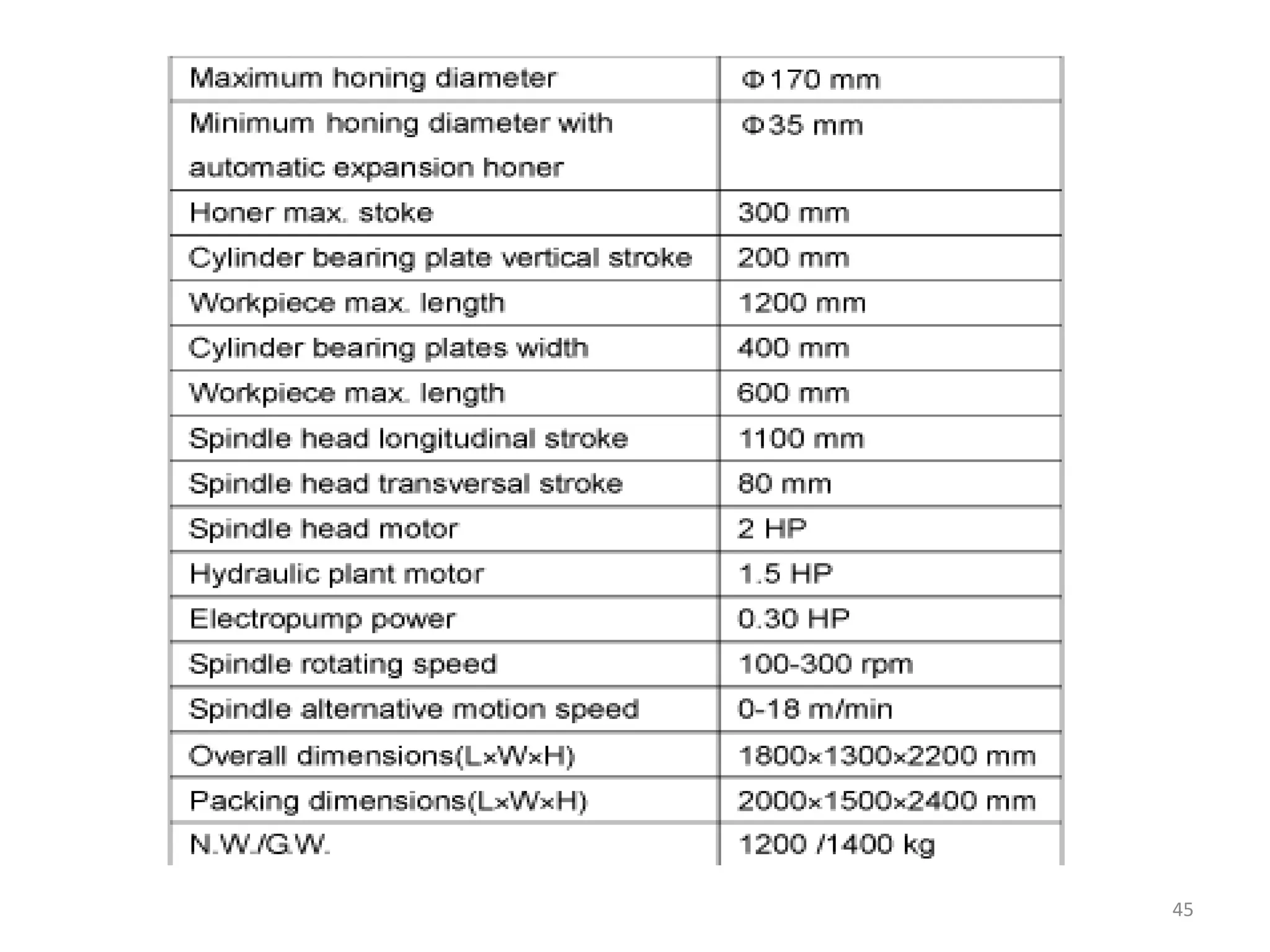
The document details the specifications and operations of various machining processes, including lapping, honing, and broaching. It explains the methods and machinery involved in lapping for polishing surfaces, honing for improving accuracy and finish, and broaching for material removal in a single stroke. It also provides specifications for different types of machines and their applications in various industrial contexts.