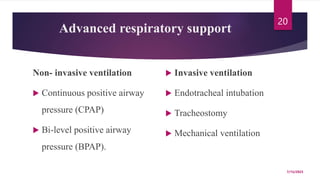
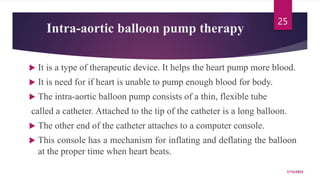
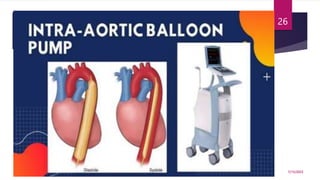
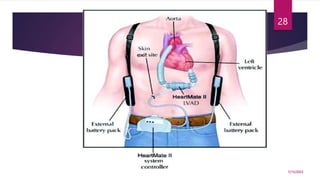
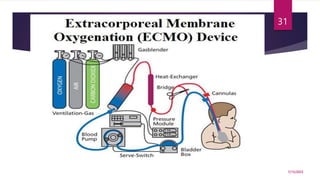
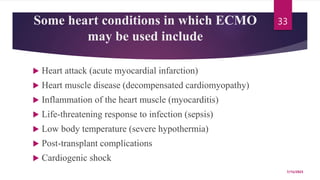
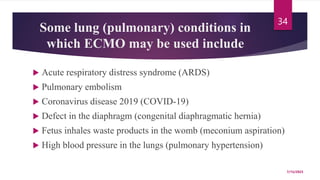
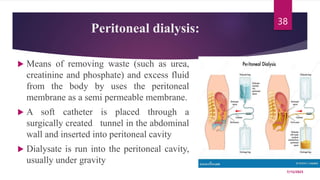
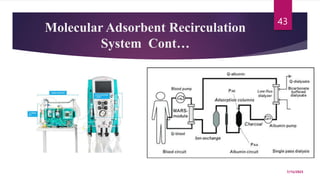
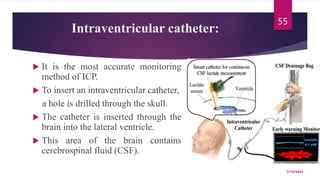
A 31-year-old man was admitted to the hospital unconscious after a car accident. Tests show increased intracranial pressure and abnormal liver and kidney function tests. Possible medical interventions include managing increased intracranial pressure, providing organ support such as ventilation if needed, and treating any organ dysfunction through interventions like dialysis.