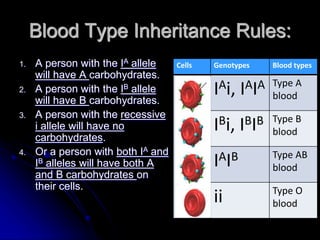
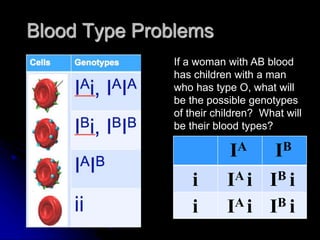
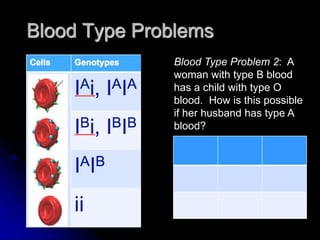
This document discusses several types of non-Mendelian genetics inheritance patterns:
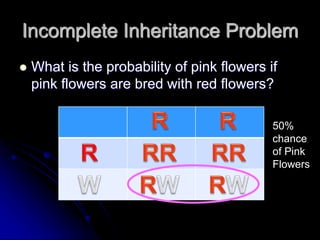
1) Incomplete dominance results in a blended phenotype between two traits when hybrids are formed rather than one trait dominating. An example is red and white flowers producing pink hybrids.
2) Codominance occurs when both alleles are fully expressed together in the hybrid phenotype. For example, a black and white cow producing a spotted hybrid.
3) Multiple alleles exist for a single trait, such as multiple coat color alleles in many animals.
4) Polygenic traits are influenced by multiple genes interacting together, like human skin tone.
5) Sex-linked traits involve genes on the sex chromosomes. Examples include color blindness,