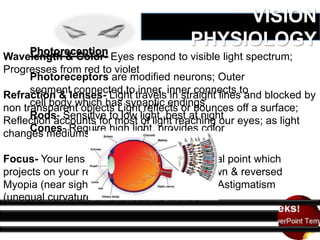
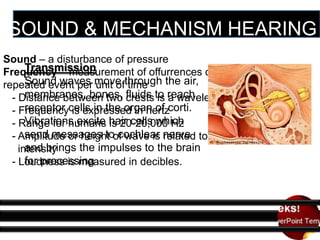
The five general senses are hearing, sight, touch, smell, and taste. Taste is detected by taste buds on the tongue that contain receptor cells. Smell occurs when chemicals dissolve in mucus in the nasal cavity and bind to odor receptors. Sight involves light refraction through the eyes and photoreception by retinal rods and cones. Hearing detects sound waves that vibrate the eardrum and small bones of the middle ear and cause fluid motions in the inner ear. Touch has no single organ but comes from receptors throughout the body, especially skin, that provide information on pressure, vibration, position, pain, and heat.