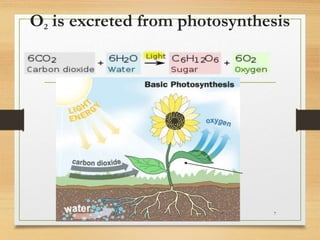
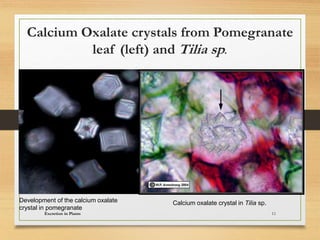
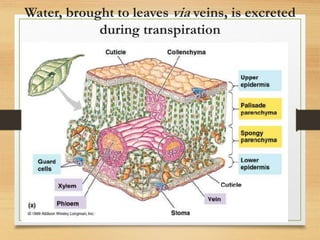
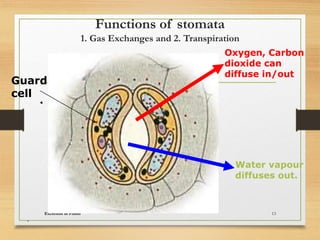
Plants excrete waste through various processes like diffusion, guttation, and leaf/tissue shedding. Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide produced during photosynthesis and respiration diffuse out through openings in bark and stomata. Excess water is excreted through guttation. Salt glands and crystals excrete salts. Calcium oxalate crystals store in and are excreted by fallen leaves. Wastes are also stored in heartwood, bark, and leaves that later die and fall off. Latex and gum can be excreted from plants. Excretion maintains plant homeostasis by removing wastes and regulating salts.