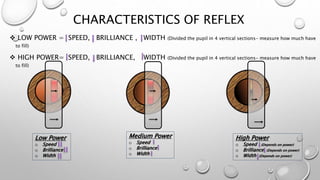
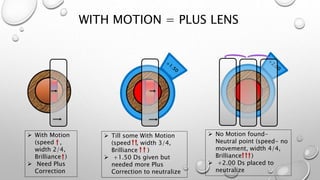
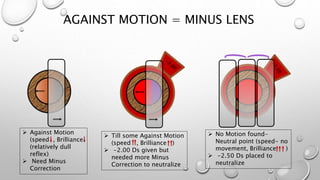
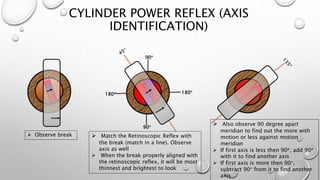
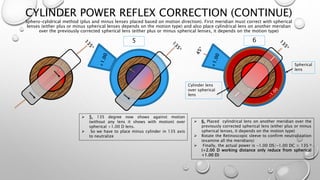
Retinoscopy is a technique used to objectively determine a patient's refractive error without their input. It involves using a retinoscope to observe the light reflex in the pupil when it is illuminated. The observer notes whether the reflex moves with or against the motion of the retinoscope, indicating whether plus or minus lenses are needed to neutralize the reflex. Additional steps are taken to determine any cylindrical error by observing the reflex in different meridians and neutralizing them with spherical and cylindrical trial lenses. The objective refraction obtained via retinoscopy provides a starting point for subjective refraction to obtain the patient's best-corrected vision.