1. The Soviet Union collapsed in 1991 due to economic and political problems including a weak economy, widespread corruption, and rising nationalism in the republics.
2. Mikhail Gorbachev's reforms of perestroika and glasnost weakened the communist party's grip on power and emboldened independence movements.
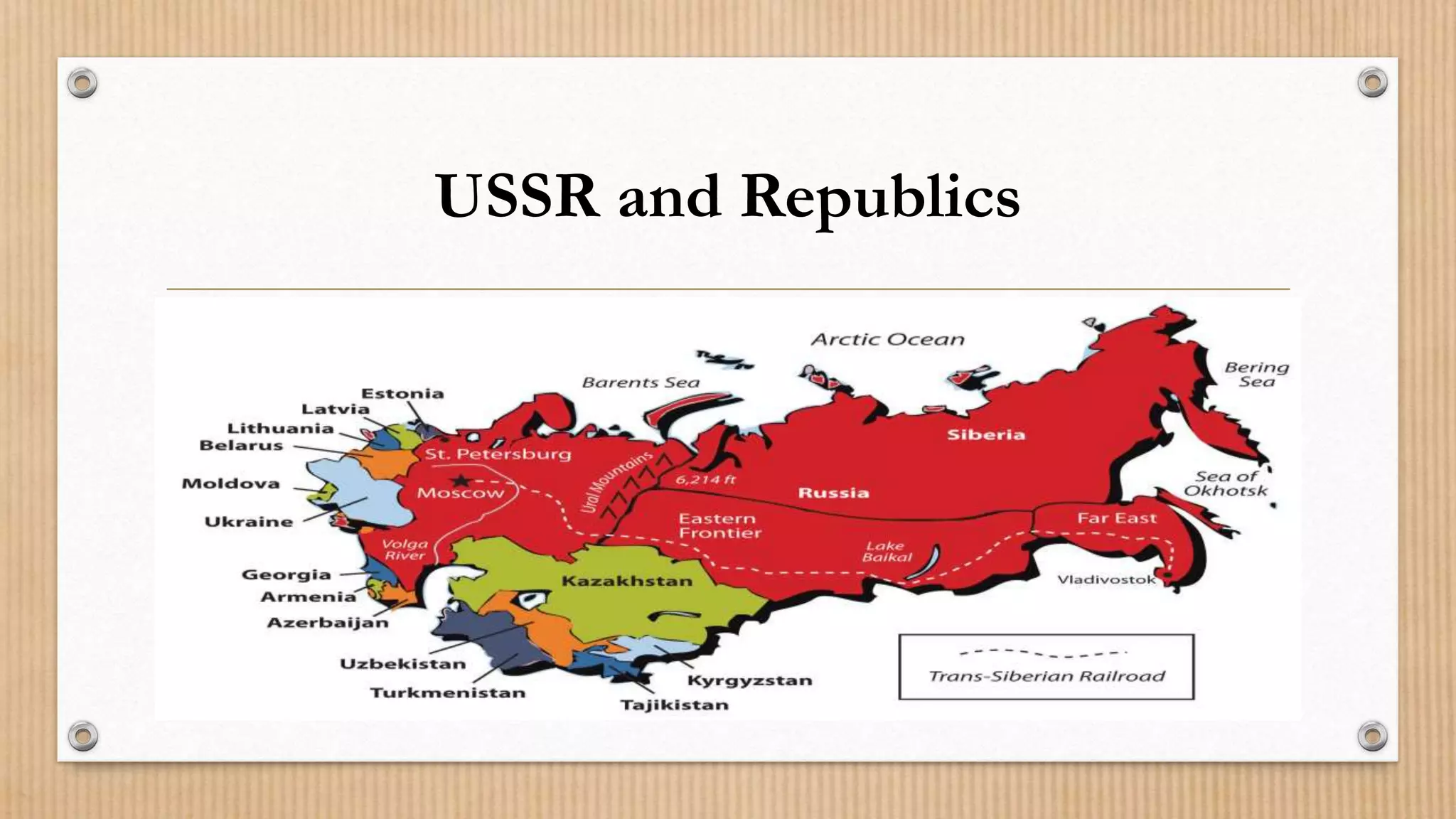
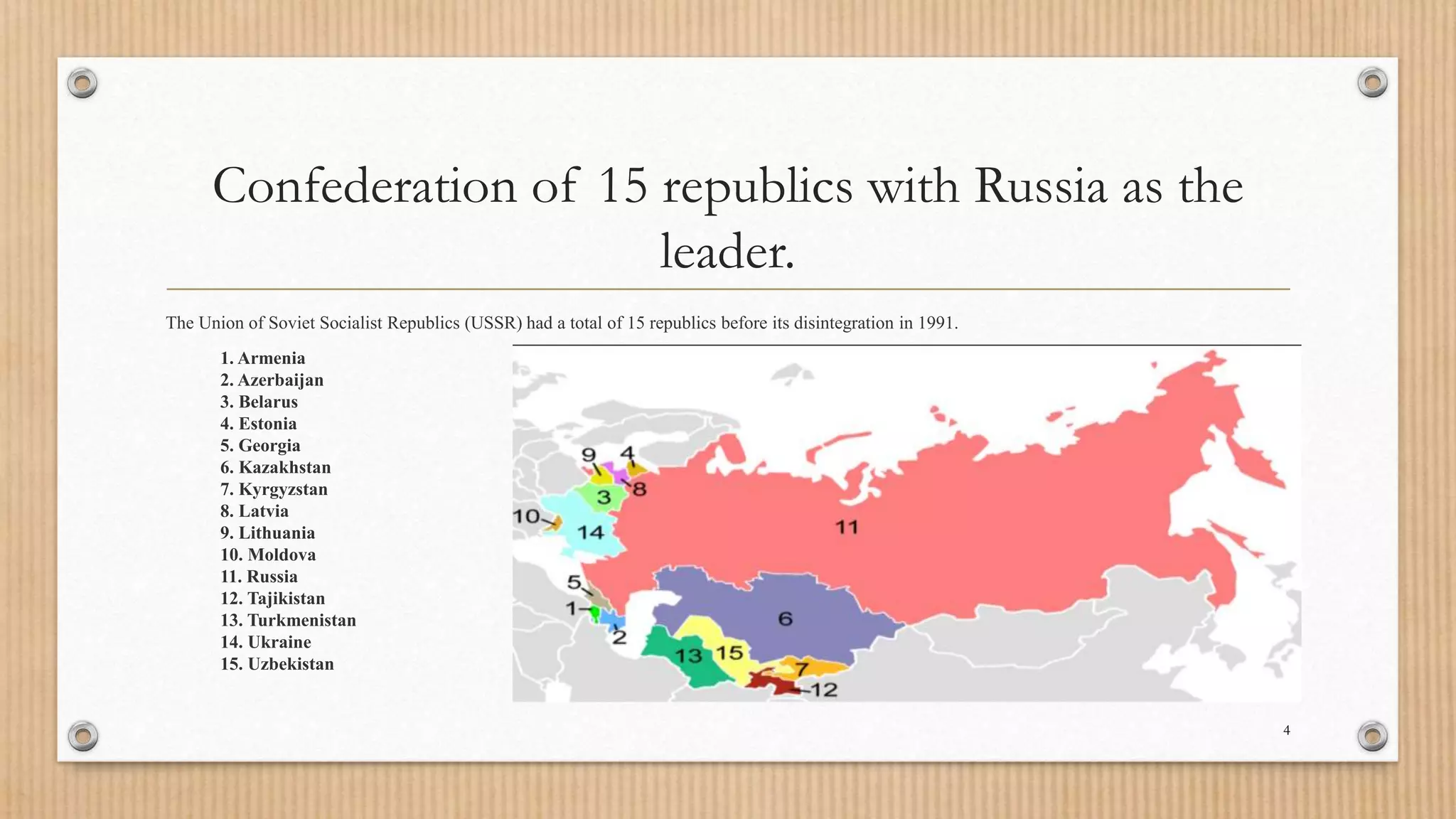
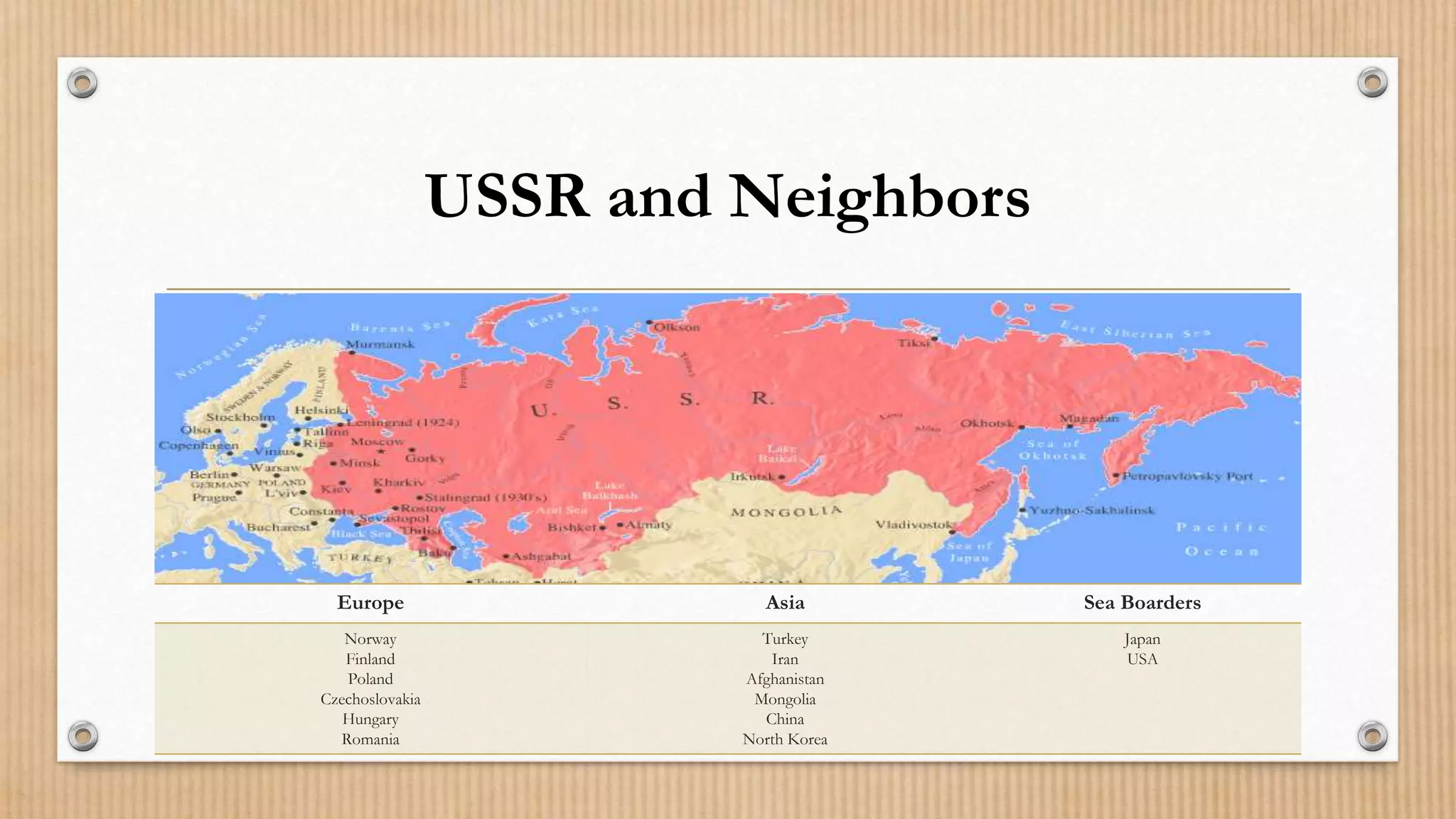
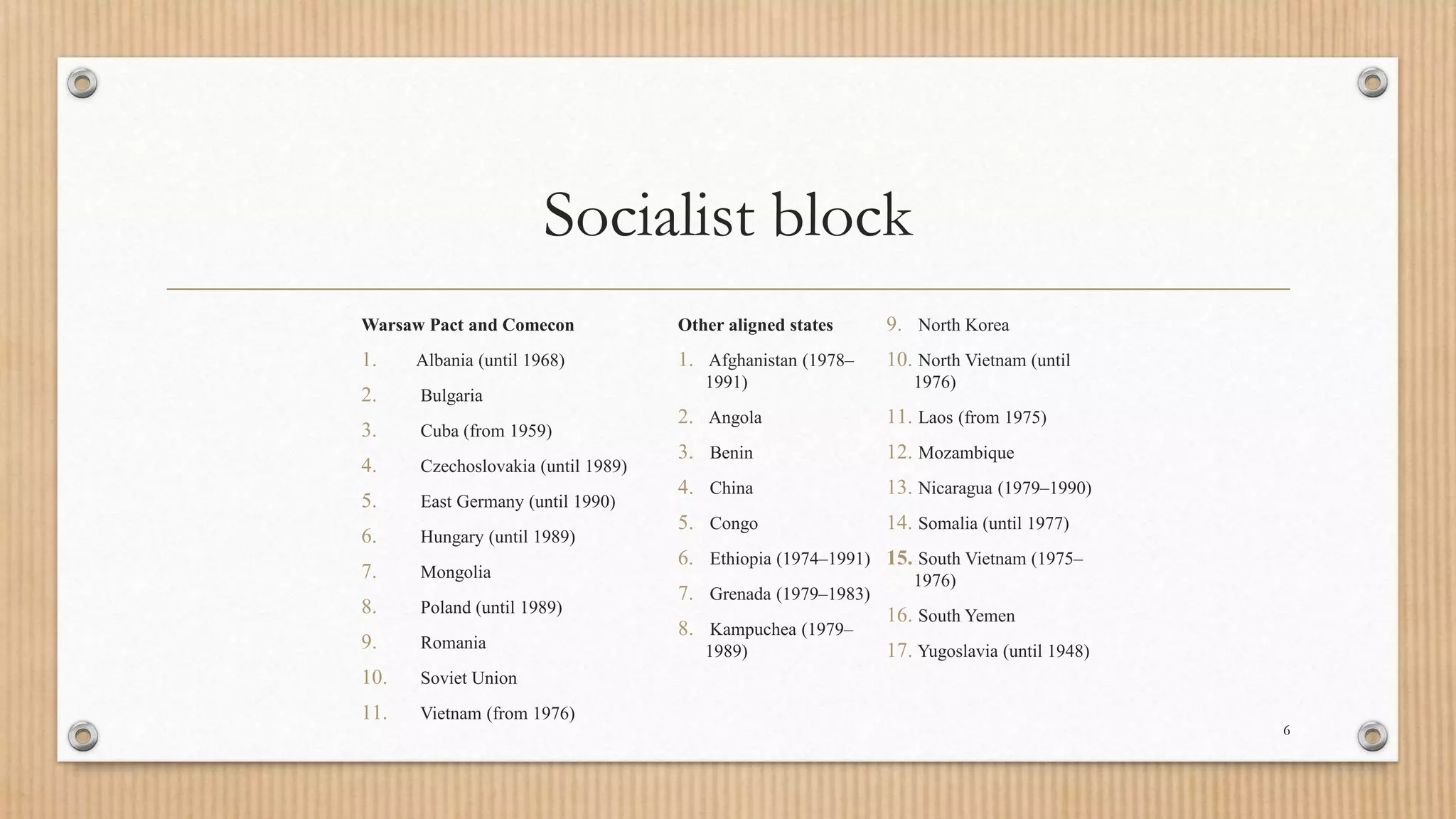
3. The Soviet war in Afghanistan and military spending drained the economy while Gorbachev's openness policies destabilized communist rule, leading to the dissolution of the USSR and formation of 15 independent republics.