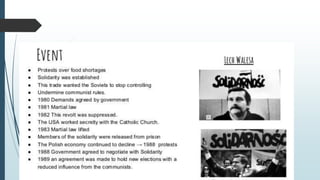
The document discusses Soviet control over Eastern Europe from 1948 to 1989. It provides background on how countries like Hungary and Czechoslovakia lost democratic rights and freedoms after World War 2 and came under strict Soviet control. It then discusses some key events that showed opposition to Soviet dominance, such as the 1956 Hungarian Uprising and the 1968 Prague Spring, and how the Soviet Union reacted with military force to maintain control each time. The building of the Berlin Wall in 1961 was also explained as an attempt to stop the flow of people from East to West Germany. Finally, the rise of the Solidarity trade union movement in communist Poland in the 1980s increased dissent and had significance for the eventual decline of Soviet influence in Eastern Europe.